Structure Sensory Neurons

Structure Of Sensory Neuron In Urdu Hindi Youtube
Types Of Neuron
Neuron Structure And Classification Brooke Hamilton Neural Tissue
Structure Of Neuron
Sensory Neuron Diagram Product Wiring Diagrams

Unipolar Neuron Structure And Functions
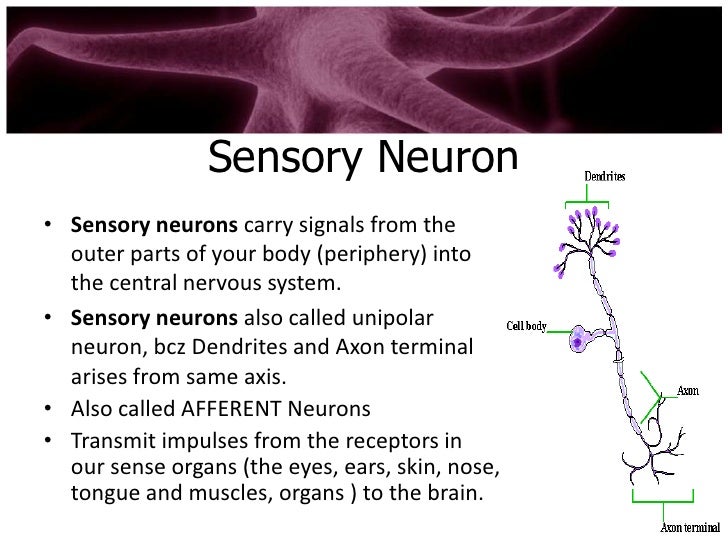
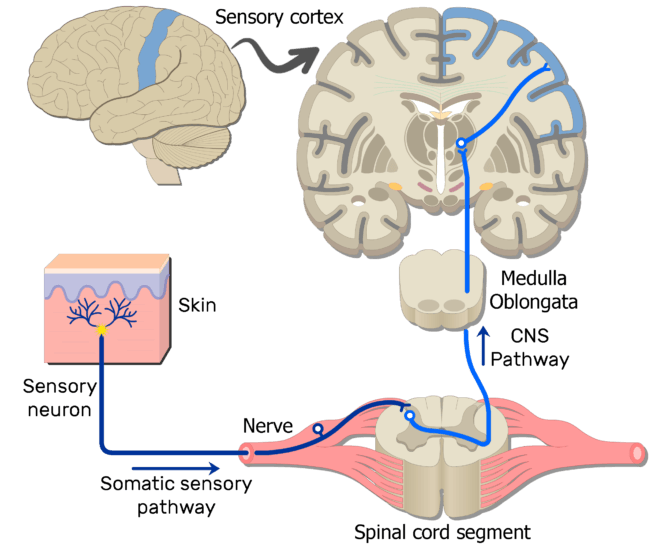
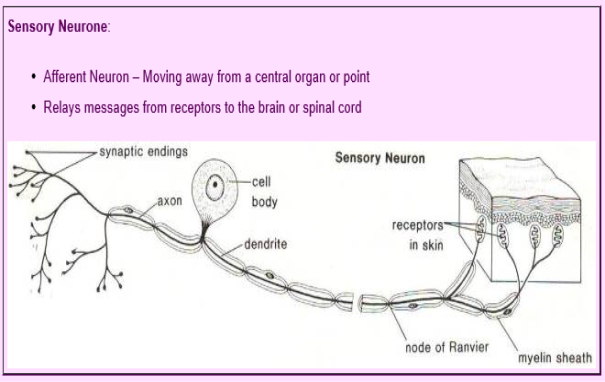
Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are the nerve cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment for example, when you touch a hot surface with your fingertips, the sensory neurons will be the ones firing and sending off signals to the rest of the nervous system about the information they have received.
Structure sensory neurons. The sensory neurons carry information from the sensory receptor cells present throughout the body to the brain Whereas, the motor neurons transmit information from the brain to the muscles The interneurons transmit information between different neurons in the body Also Read Nervous System Neuron Structure. The body of the cerebellum holds more neurons than any other structure of the brain, including that of the larger cerebrum, but is also more extensively understood than other structures of the brain, as it includes fewer types of different neurons It handles and processes sensory stimuli, motor information, as well as balance information from. Complete receptor cells, which are specialized epithelial cells or small neurons that transfer sensory information to sensory neurons.
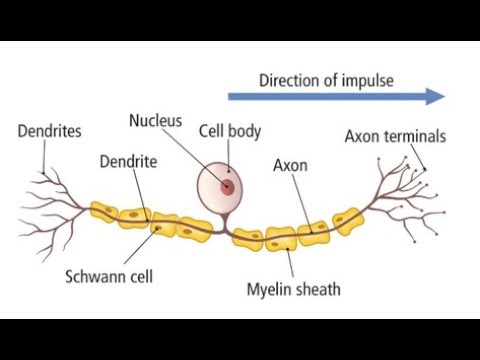
As such, it differs greatly from most cells Structures known as dendrites are at one end of the nerve cell;. Singlecell transcriptomes of olfactory receptor neurons at multiple developmental stages reveal celltypespecific gene expression programs that underlie their development and sensory biology. The nerves cells are rather long which enables communication with distant body parts The dendrites allow for communication with other neurons Myelin surrounding the axon of a neuron acts as an insulator The above example is a very general description In fact, neurons can be categorized into three groups based on their function Sensory neurons Carry impulses from the receptors (cells that.
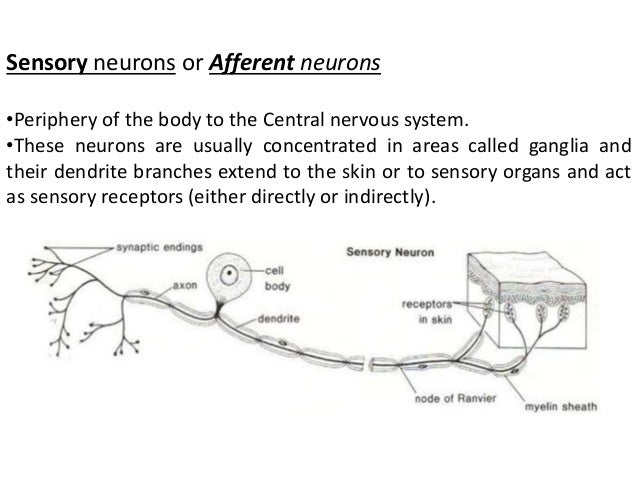
Which monitor outside environment and our position, (2) Visceral sensory neurons;. Neurons having free sensory endings are a heterogeneous group whose morphology is difficult to characterize Currently, sensory neurons innervating the skin are classified using several features morphology, conductance, sensory modalities, and molecular markers Encapsulated sensory endings are associated with fast conducting fibers (ie. Structure of Sensory Receptors As a matter of fact, the sensory receptors are the ends of dendritic sensory neurons The sensory neurons make up sensory nerve bundles which are characterized by their ability to send or transmit a message to the brain The structure of sensory receptors can vary according to their location or function.
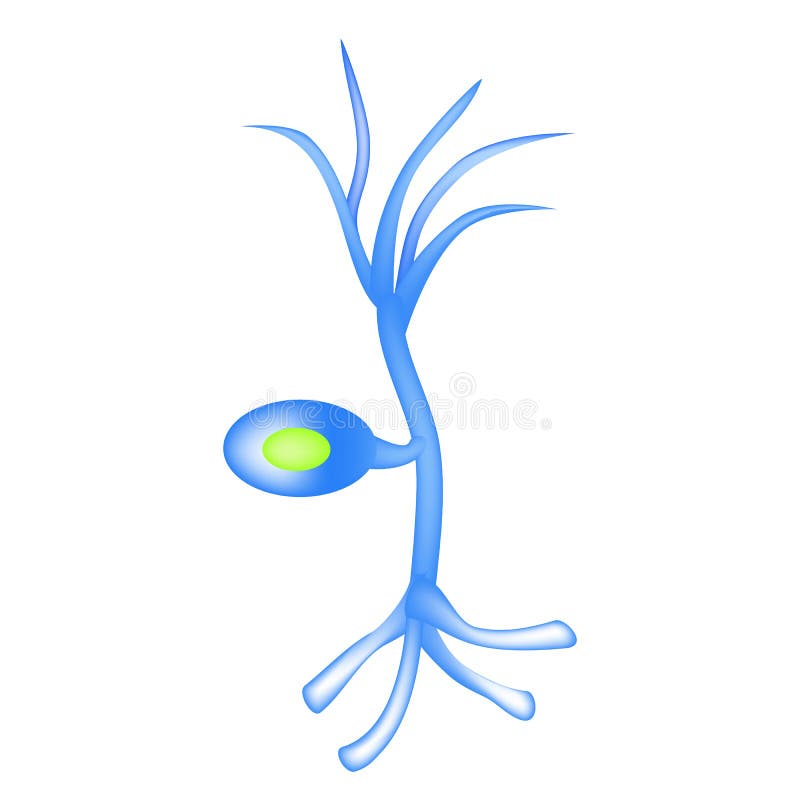
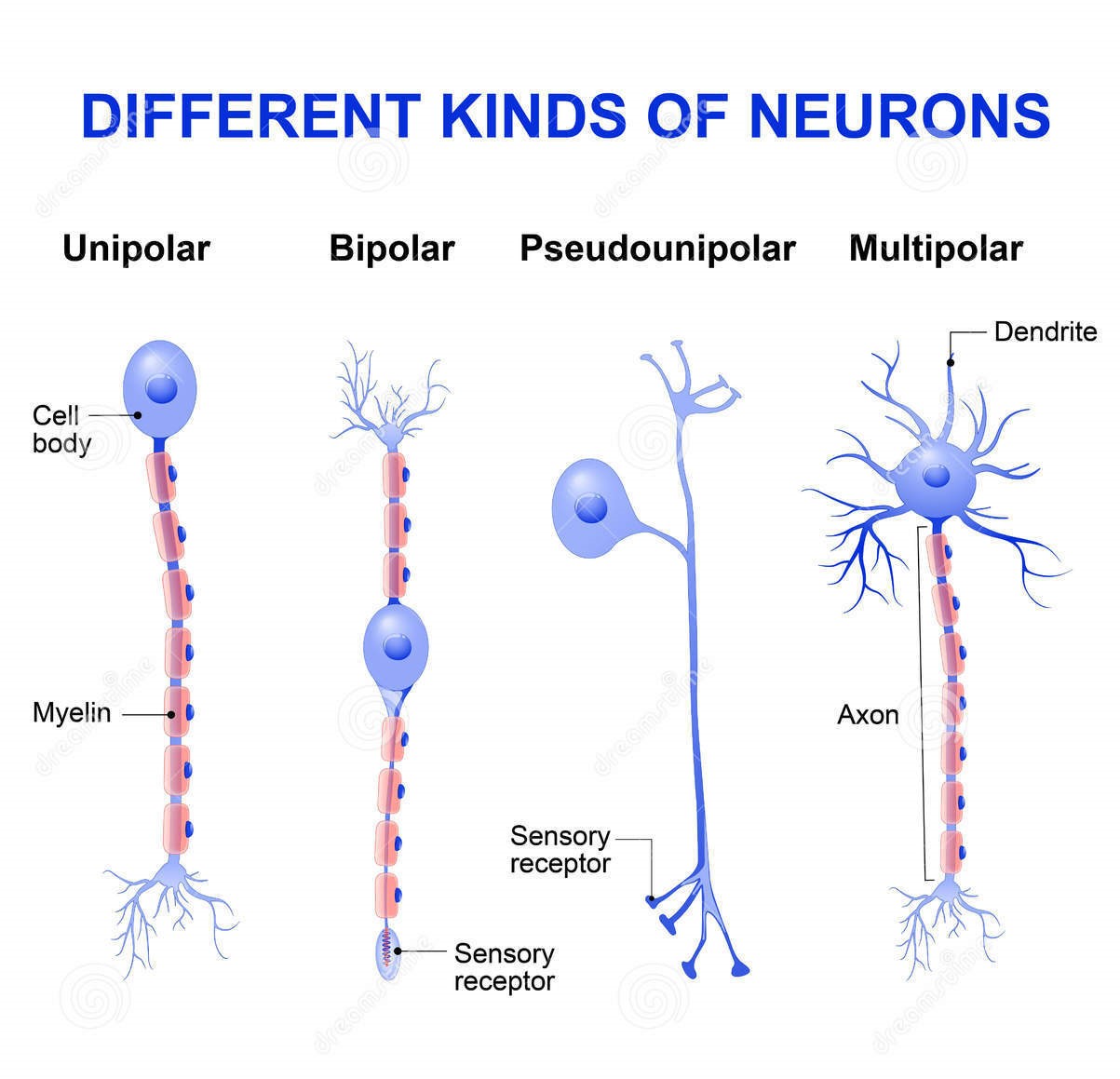
Well most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar, meaning they have an axon that branches into two extensions—one connected to dendrites that receive sensory information and. Structure of Sensory Neurons Image will be Uploaded Soon Sensory neuron s conduct signals from sensory organs to the CNS Sensory Neurons arise from the dorsal root ganglion, which are specialized clusters present at the dorsal roots of the spinal cord Sensory neurons lack distinct axons and dendrites Sensory neurons possess receptors. Complete receptor cells, which are specialized epithelial cells or small neurons that transfer sensory information to sensory neurons.
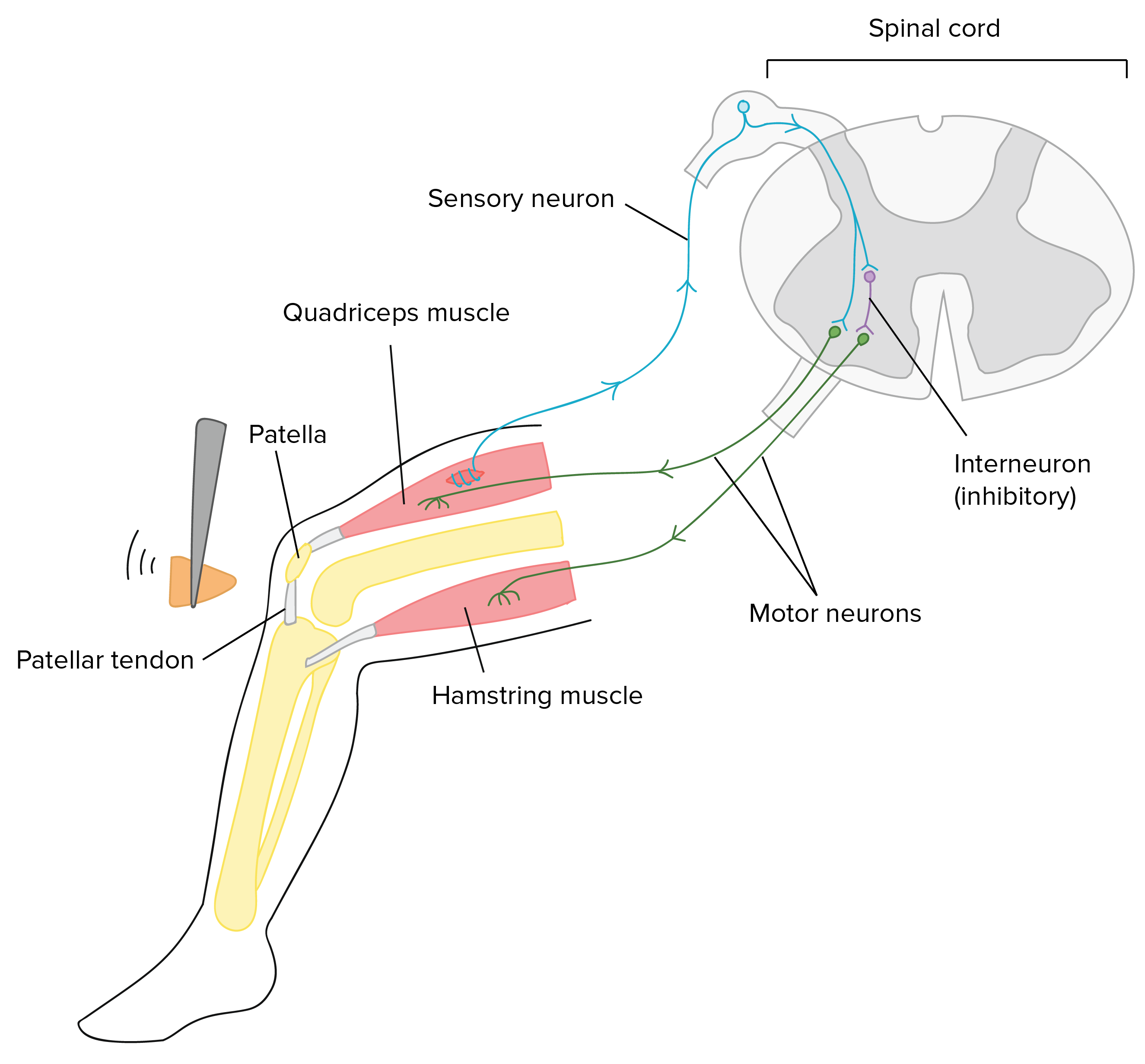
The sensory neurons transmit the information to the spinal cord, where a signal is sent to motor neurons The motor neurons then cause the quadriceps muscles to contract, causing the kicking motion In this example, interneurons are not involved, as there is a direct connection between the sensory and motor neurons. Structure of Sensory Receptors As a matter of fact, the sensory receptors are the ends of dendritic sensory neurons The sensory neurons make up sensory nerve bundles which are characterized by their ability to send or transmit a message to the brain The structure of sensory receptors can vary according to their location or function. Start studying PNS 1 Nerve Structure & Sensory Neurons Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The body of the cerebellum holds more neurons than any other structure of the brain, including that of the larger cerebrum, but is also more extensively understood than other structures of the brain, as it includes fewer types of different neurons It handles and processes sensory stimuli, motor information, as well as balance information from. Singlecell transcriptomes of olfactory receptor neurons at multiple developmental stages reveal celltypespecific gene expression programs that underlie their development and sensory biology. (1) Somatic sensory neurons;.
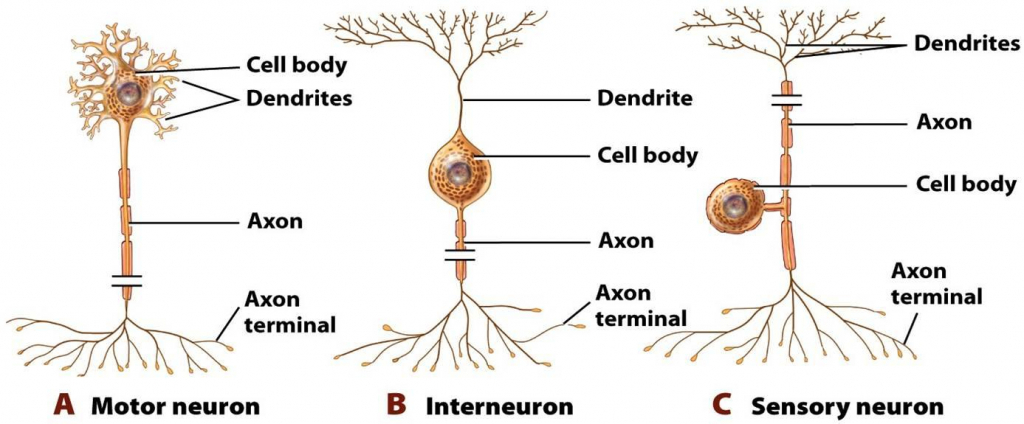
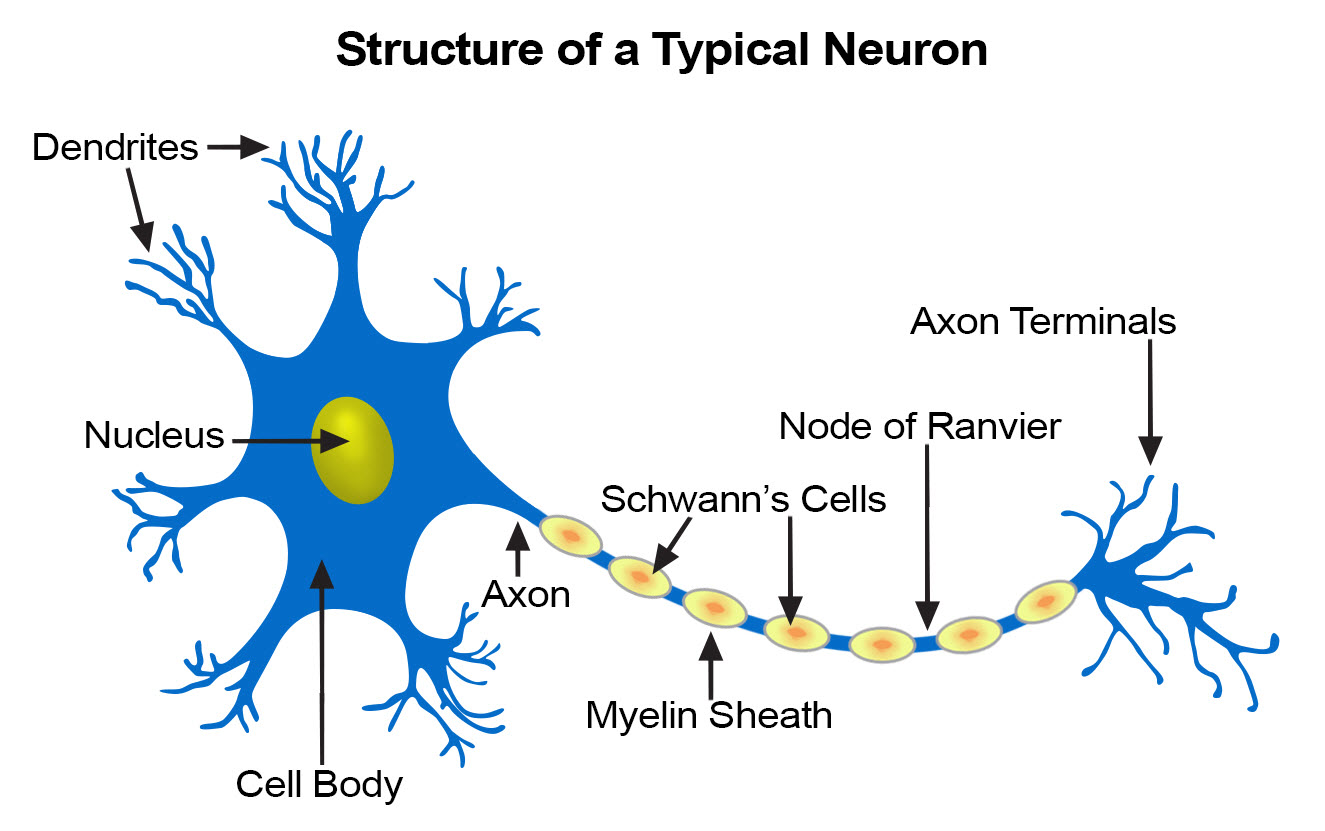
The dendrites of neurons receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons This information is then passed down to the cell body and on to the axon Once the information has arrived at the axon, it travels down the length of the axon in the form of an electrical signal known as an action potential. Receptor cell types can be classified on the basis of their structure Sensory neurons can have either (a) free nerve endings or (b) encapsulated endings Photoreceptors in the eyes, such as rod cells, are examples of (c) specialized receptor cells These cells release neurotransmitters onto a bipolar cell, which then synapses with the optic. There are three main types of neurons, including sensory, relay and motor Each of these neurons has a different function, depending on its location in the body and its role within the nervous system NoteAll three types of neuron consist of similar parts, however their structure, location and.
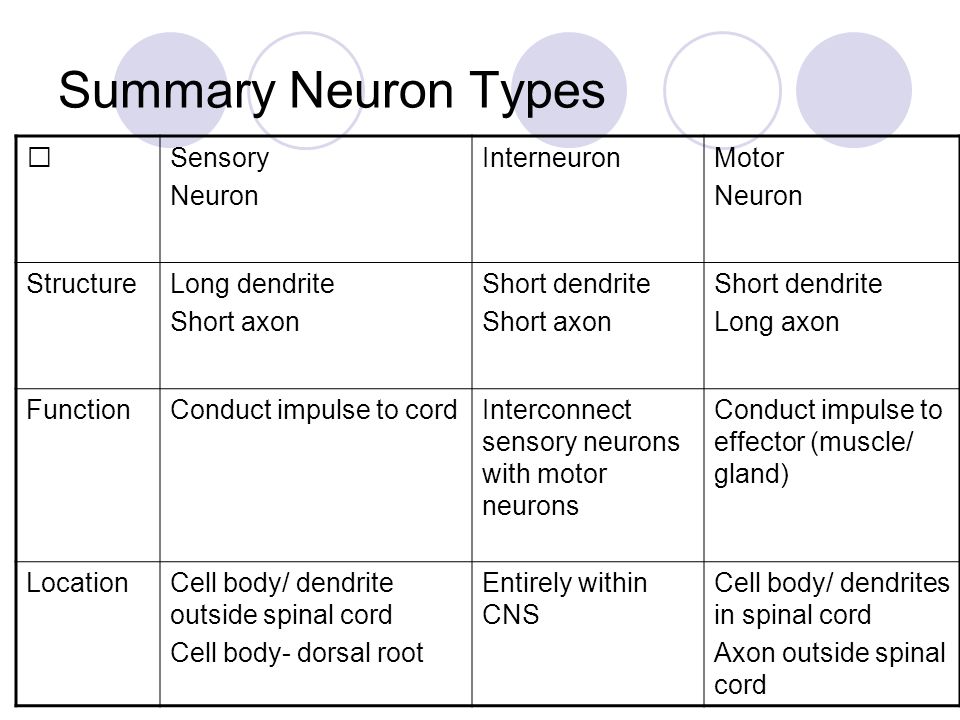
Neurons can also be divided on the basis of the functions they perform On this basis, there are THREE types of neurons They are Sensory Neurons;. Interneurons, sensory neurons, and motor neurons. The Structure and Function of Sensory, Relay and Motor Neurons The nervous system is composed of specialised cells called neurons The neurons form pathways in the brain.
Which monitor internal body conditions and the status of organ systems. The sensory neurons transmit the information to the spinal cord, where a signal is sent to motor neurons The motor neurons then cause the quadriceps muscles to contract, causing the kicking motion In this example, interneurons are not involved, as there is a direct connection between the sensory and motor neurons. Neurons can be classified by function or by structure Functionally, they fall into three groups Sensory neurons ( afferent neurons) transmit sensory impulses from the skin and other sensory organs or from various places within the body toward the central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord.
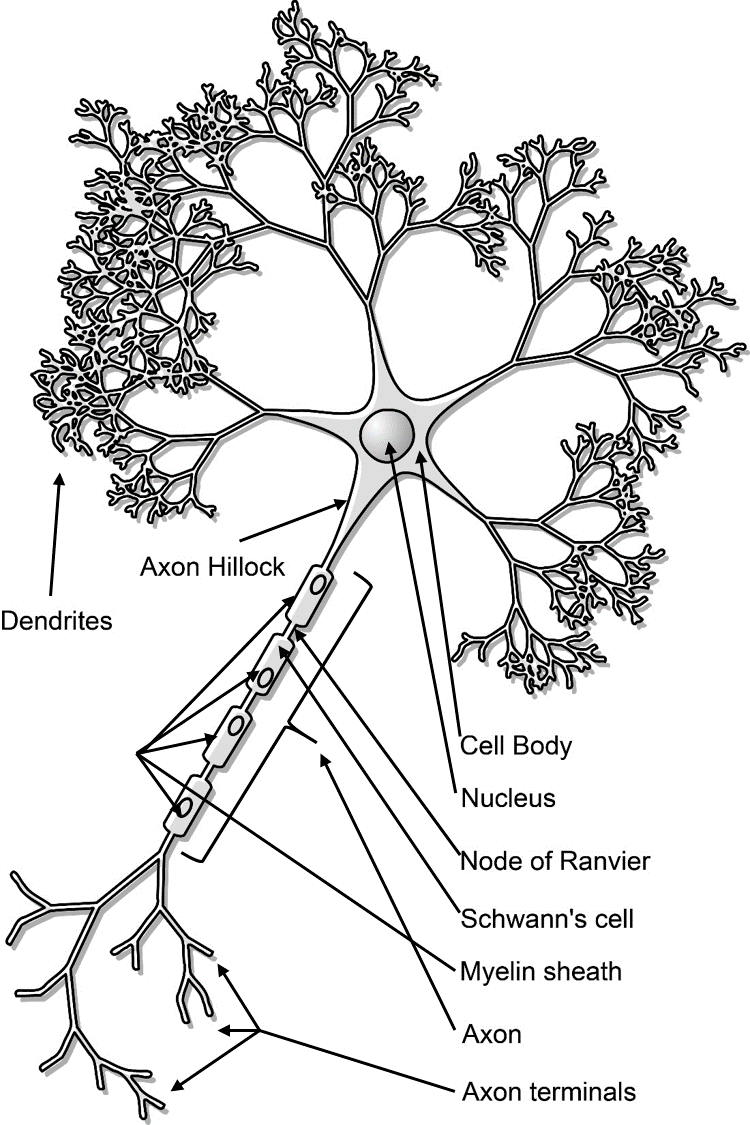
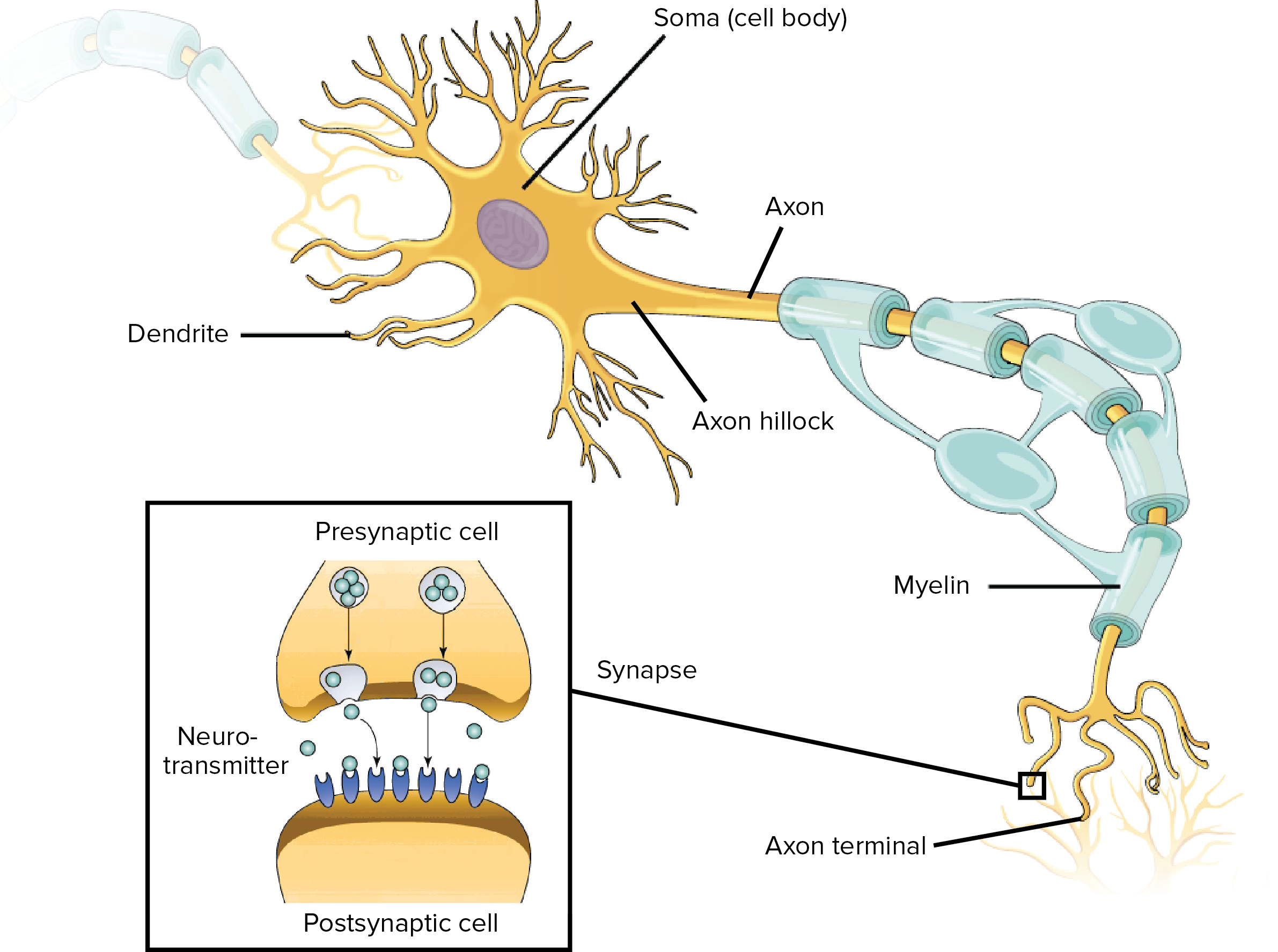
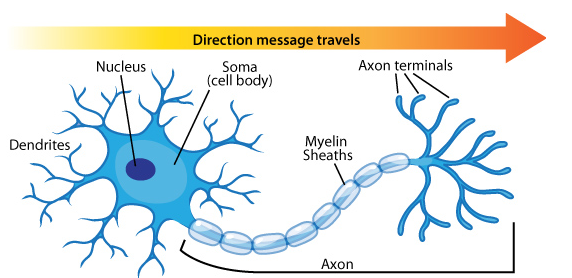
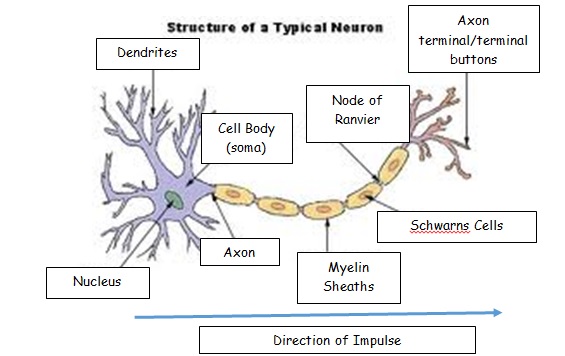
Cell body Also known as a soma, the cell body is the neuron’s core The cell body carries genetic information, maintains the neuron’s structure, and. 22 Sensory Neurons are those Neurons that will pick up information from sensory receptors on body, for example – Ears, Tongue, Eyes, Skin, Nose etc. Unipolar neurons are found primarily in the afferent division of the PNS Functional Classification of Neurons Neurons are classified functionally according to.
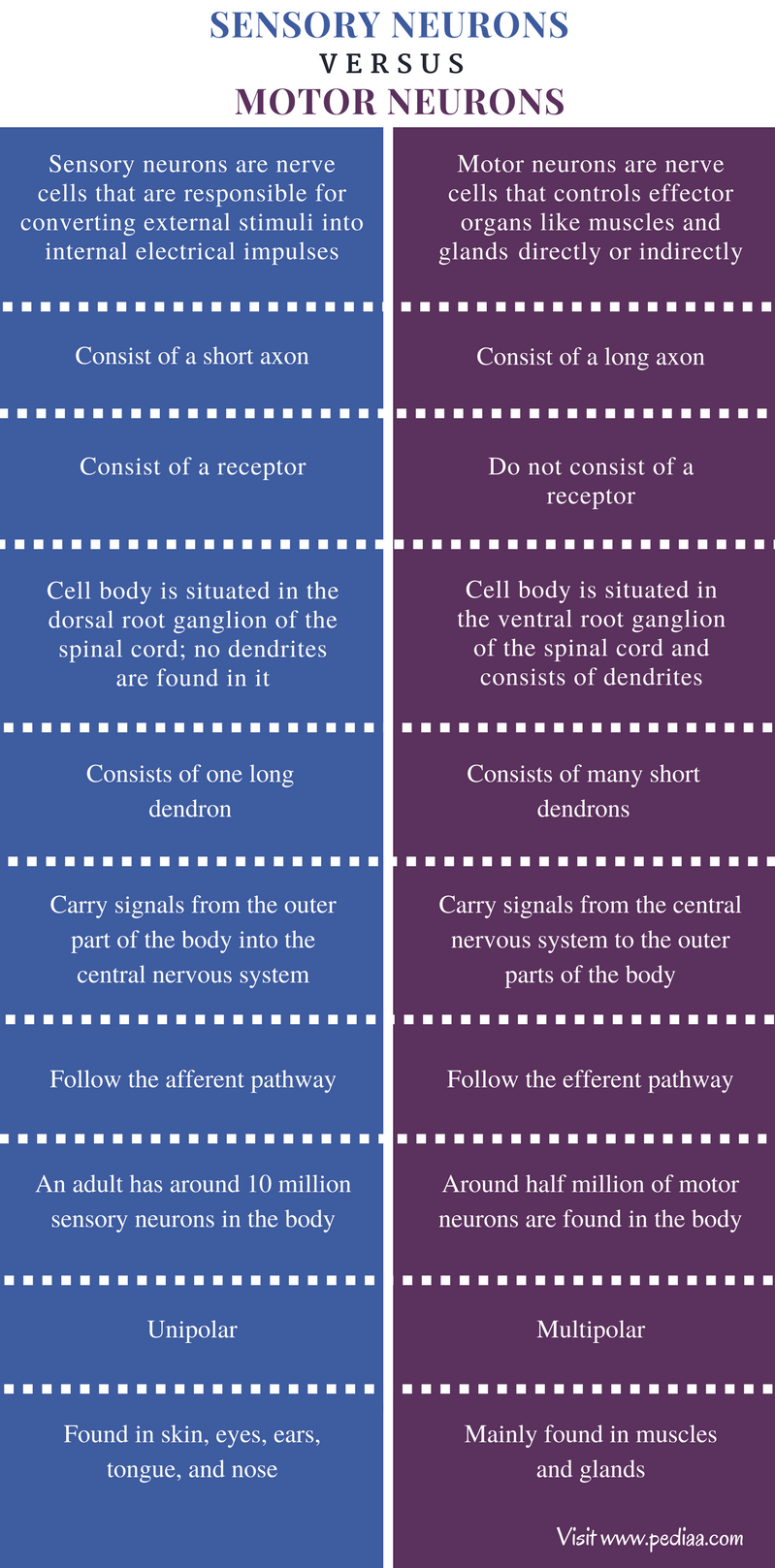
Structure of Sensory Receptors As a matter of fact, the sensory receptors are the ends of dendritic sensory neurons The sensory neurons make up sensory nerve bundles which are characterized by their ability to send or transmit a message to the brain The structure of sensory receptors can vary according to their location or function. Sensory neurons are neurons responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into corresponding internal stimuli Motor neurons are neurons located in. The body of the cerebellum holds more neurons than any other structure of the brain, including that of the larger cerebrum, but is also more extensively understood than other structures of the brain, as it includes fewer types of different neurons It handles and processes sensory stimuli, motor information, as well as balance information from.
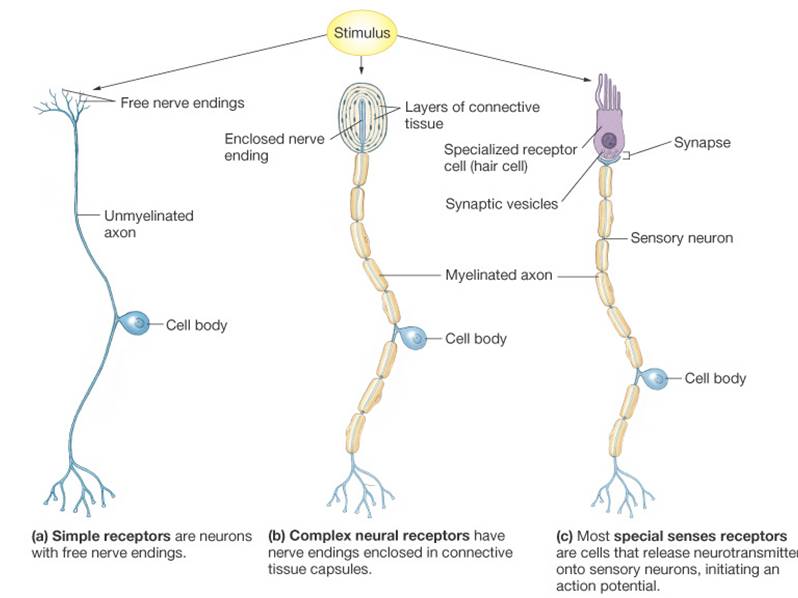
Figure 1311 – Receptor Classification by Cell Type Receptor cell types can be classified on the basis of their structure Sensory neurons can have either (a) free nerve endings or (b) encapsulated endings Photoreceptors in the eyes, such as rod cells, are examples of (c) specialized receptor cells. Sensory afferent neuron s convey information from tissues and organs into the CNS (central nervous system), while efferent neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to the effector cells Interneurons connect neurons within specific regions of the central nervous system. Receptor cell types can be classified on the basis of their structure Sensory neurons can have either (a) free nerve endings or (b) encapsulated endings Photoreceptors in the eyes, such as rod cells, are examples of (c) specialized receptor cells These cells release neurotransmitters onto a bipolar cell, which then synapses with the optic.
Sensory neurons (afferent neurons) are unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar shaped cells that conduct action potentials toward or into the central nervous system They carry somatic nervous system signals from the skin, joints, skeletal muscles, sensory organs ( eyes, ears, mouth, and nose ). Peripheral sensory receptors are structures that pick up sensory stimuli and then initiate signals in the sensory axons Most receptors fit into two main categories Free nerve endings of sensory neurons and;. Which monitor internal body conditions and the status of organ systems.
Sensory neurons help the brain react to various stimuli, such as touch A neuron is a cell that is specialized to carry neural information throughout the body;. The main difference between sensory and motor neuron is their function and structure Both these neurons enable the central nervous system to coordinate different functions in the body Also Read Difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic. In human nervous system Enteric nervous system intrinsic enteric neurons are recognized sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons Sensory neurons, activated by either mechanical or chemical stimulation of the innermost surface of the gut, transmit information to interneurons located within the Auerbach and the Meissner plexi, and the interneurons relay the information to motor.
Receptor cell types can be classified on the basis of their structure Sensory neurons can have either (a) free nerve endings or (b) encapsulated endings Photoreceptors in the eyes, such as rod cells, are examples of (c) specialized receptor cells These cells release neurotransmitters onto a bipolar cell, which then synapses with the optic. Peripheral sensory receptors are structures that pick up sensory stimuli and then initiate signals in the sensory axons Most receptors fit into two main categories Free nerve endings of sensory neurons and;. Moreover, the sensory neurons gather information from external and internal environments through sensory receptors Accordingly, sensory neurons can be divided into two types;.
Sensory neurons help the brain react to various stimuli, such as touch A neuron is a cell that is specialized to carry neural information throughout the body;. Location, Structure, and Functions of Sensory Neurons With Diagrams SENSORY NEURONS They convert external sensory stimuli like touch, pain, sense of heat, smell, as. Sensory Neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that are located within the nervous system and which are responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment of the organism into electrical impulses that are internal This process is part of functions that include muscle contractions and even involuntary behaviors such as pain.
Types of Sensory Neurons Olfactory sensory neurons are bipolar neurons located in the nasal cavity They are activated by odor molecules in the air and give us our. Peripheral sensory receptors are structures that pick up sensory stimuli and then initiate signals in the sensory axons Most receptors fit into two main categories Free nerve endings of sensory neurons and;. Which monitor outside environment and our position, (2) Visceral sensory neurons;.
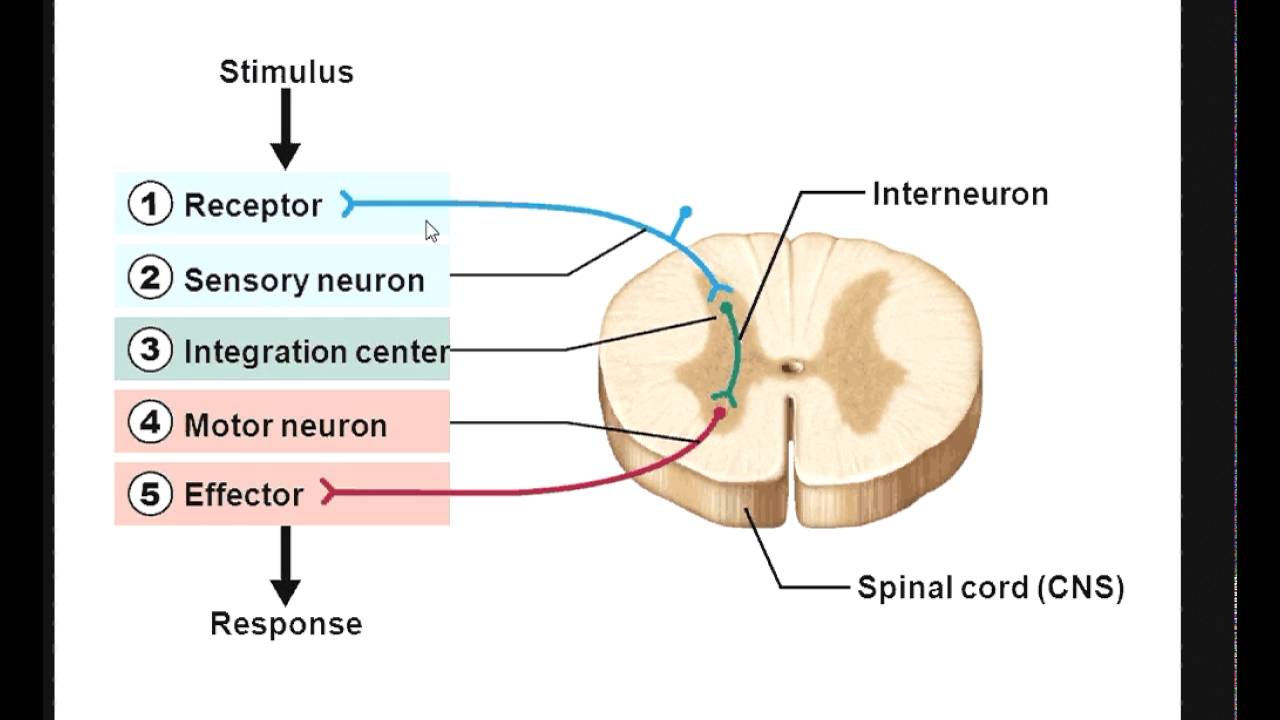
The basic functions of a neuron Receive signals (or information) Integrate incoming signals (to determine whether or not the information should be passed along). Neurons are also frequently classified by their function Such as sensory neurons, afferent neurons which carry information about the internal and external world to the central nervous system They occur in places such as specialized sense organs eyes, inner ear, skin, nose, tongue, joints. Structure of Sensory Neurons A typical neuron is comprised of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body, and the sensory neurons are no exception Most sensory.
Neurons are also frequently classified by their function Such as sensory neurons, afferent neurons which carry information about the internal and external world to the central nervous system They occur in places such as specialized sense organs eyes, inner ear, skin, nose, tongue, joints. On the basis of function neurons are mainly two types 1 Sensory neuron and 2 Motor neuronInterneurons are also included in this type STRUCTURE OF A TYPICAL NEURON A typical neuron primarily consist of the Cell body and processes, also called neurites Neurites are two types – A Dendrites and B Axon. 22 Sensory Neurons are those Neurons that will pick up information from sensory receptors on body, for example – Ears, Tongue, Eyes, Skin, Nose etc.
Singlecell transcriptomes of olfactory receptor neurons at multiple developmental stages reveal celltypespecific gene expression programs that underlie their development and sensory biology. Sensory Neuron Sensory neurons also referred to as afferent neurons, are nerve cells within the nervous system responsible for converting external stimuli from an. The sensory neurons receive stimuli from sensory organs that monitor the external and internal environment of the body Depending on their specialized functions, the sensory neurons convey messages about factors such as heat, light, pressure, muscle tension, and odor to higher centers in the nervous system for processing.
Moreover, the sensory neurons gather information from external and internal environments through sensory receptors Accordingly, sensory neurons can be divided into two types;. As such, it differs greatly from most cells Structures known as dendrites are at one end of the nerve cell;. (1) Somatic sensory neurons;.
Sensory Neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that are located within the nervous system and which are responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment of the organism into electrical impulses that are internal This process is part of functions that include muscle contractions and even involuntary behaviors such as pain. Unipolar neurons are found primarily in the afferent division of the PNS Functional Classification of Neurons Neurons are classified functionally according to the direction in which the signal travels, in relation to the CNS This classification also results in three different types of neurons sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Structure and Functions of Neuron Overview Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS The cell bodies of some PNS neurons, such as the motor neurons that control skeletal muscle, the type of muscle found in your arm or leg, are located in the CNS.
The sensory neurons transmit the information to the spinal cord, where a signal is sent to motor neurons The motor neurons then cause the quadriceps muscles to contract, causing the kicking motion In this example, interneurons are not involved, as there is a direct connection between the sensory and motor neurons. The body of the cerebellum holds more neurons than any other structure of the brain, including that of the larger cerebrum, but is also more extensively understood than other structures of the brain, as it includes fewer types of different neurons It handles and processes sensory stimuli, motor information, as well as balance information from. Difference Between Sensory and Motor Neurons Definition Sensory Neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that are responsible for converting external stimuli into internal electrical impulses Motor Neurons Motor neuron is a nerve cell whose cell body is located in the spinal cord and axon fiber projects outside of the spinal cord It directly or indirectly controls effector organs like.
Neurons can also be divided on the basis of the functions they perform On this basis, there are THREE types of neurons They are Sensory Neurons;. The main difference between sensory and motor neuron is their function and structure Both these neurons enable the central nervous system to coordinate different functions in the body Also Read Difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic. Being the most basic units of the human nervous system, neurons play a vital role in sensing and responding to different external as well as internal stimuli A motor neuron is one of the three types of neurons involved in this process Read about the structure and function of a motor neuron with reference to a neatly labeled diagram, in this Bodytomy post.
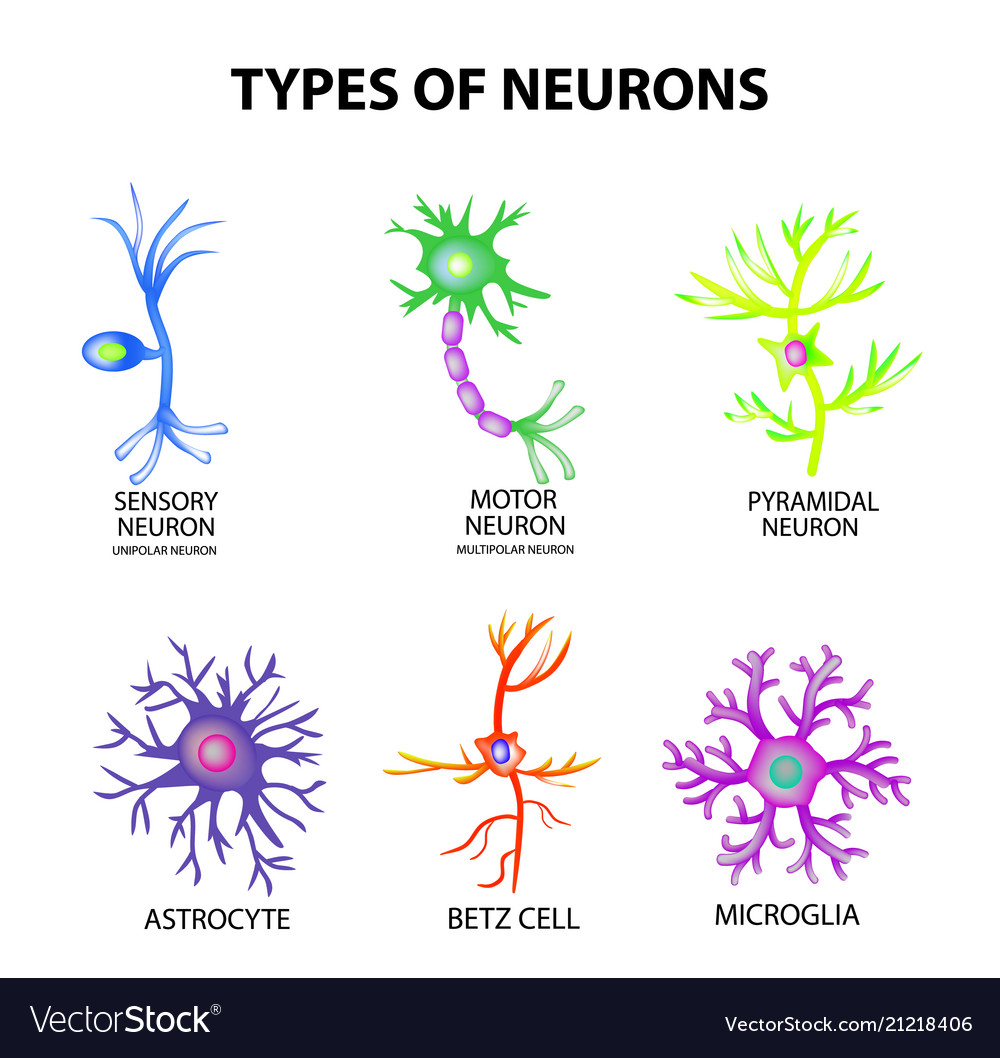
Structure of Sensory Receptors As a matter of fact, the sensory receptors are the ends of dendritic sensory neurons The sensory neurons make up sensory nerve bundles which are characterized by their ability to send or transmit a message to the brain The structure of sensory receptors can vary according to their location or function. Neurons are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system They are responsible for carrying and processing information from different parts of the body Neurons are classified into three major classes based on their functions;. Neurons are a type of cell and are the fundamental constituents of the nervous system and brain Neurons take in stimuli and convert them to electrical and chemical signals that are sent to our brain There are 3 major kinds of neurons in the spinal cord sensory, motor, and interneurons.
The sensory neurons transmit the information to the spinal cord, where a signal is sent to motor neurons The motor neurons then cause the quadriceps muscles to contract, causing the kicking motion In this example, interneurons are not involved, as there is a direct connection between the sensory and motor neurons.
Nerve Cells The Neuron Ppt Download

6 2 Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neuron Flashcards Quizlet
Q Tbn And9gcq7aaf8bmfhts9odkda1mwuxgeglnu5evwitukmyrprmtutfbak Usqp Cau

Neurons In The Nervous System Brain Anatomy Brain Neurons Neuroscience

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

5 8 1 Describe The Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neurones Including The Role Of Schwann Cells And Myelination A Biology
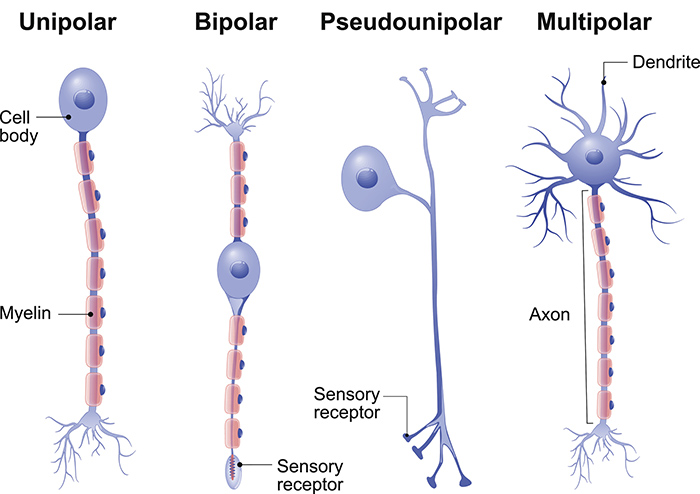
Types Of Neurons Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland

Sensory Neuron An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

What Is The Difference Between Sensory Neuron And Motor Neuron Brainly In

13 1 Sensory Receptors Anatomy Physiology
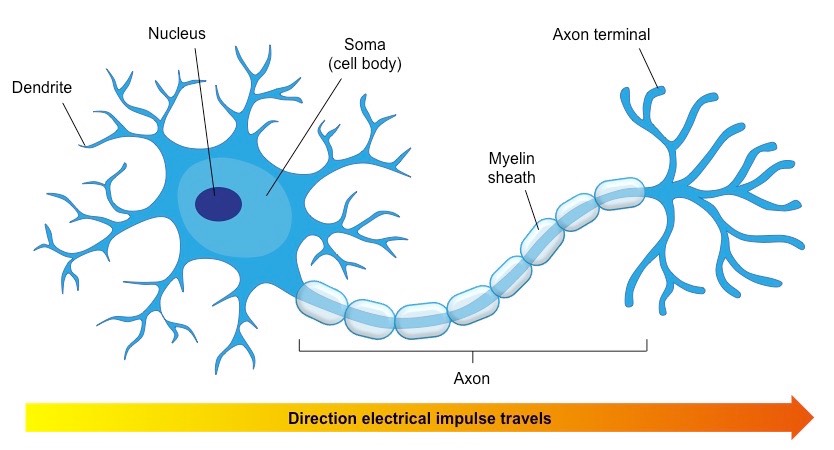
How Is A Neuron Adapted To Perform Its Function Socratic

Basic Sciences Structure Of A Sensory Neuron Youtube

Neurons Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Motor Neurones Sensory Neurones And Relay Neurones
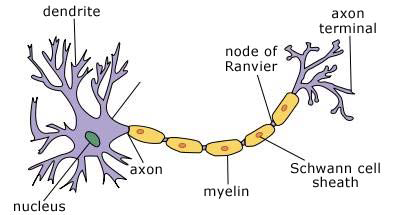
Cybersurgeons
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
Sensory Neurons Location Pictures The Structure Of The Sensory Neuron Infographics Vector

Structure Sensory Neuron Infographics Royalty Free Vector

Afferent Nerve Fiber Wikipedia

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
How To Draw Sensory Neuron Well Labelled And Very Easy Youtube

Neurons
The Structure Of The Sensory Neuron Infographics Vector Illustration On Isolated Background Stock Vector Illustration Of Diagram Cord

Sensory Neuron Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Types Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Vector Image
Biol 237 Class Notes Neurology

Doc A The Structure Of A Neuron Guvvala Reddy Academia Edu
Do Motor Neurons Have The Same Structure As Sensory Neurons Quora
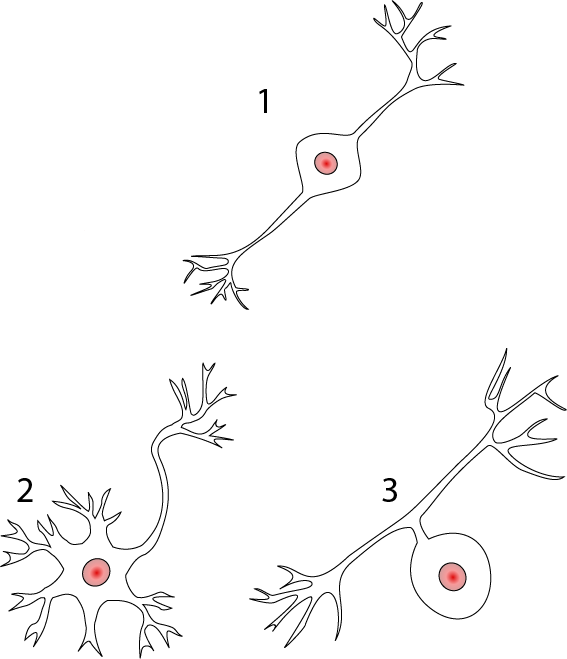
3
Q Tbn And9gct9yycisgxxqqrh9bdzlunzk8h1e Wefctwea2dwpk Usqp Cau
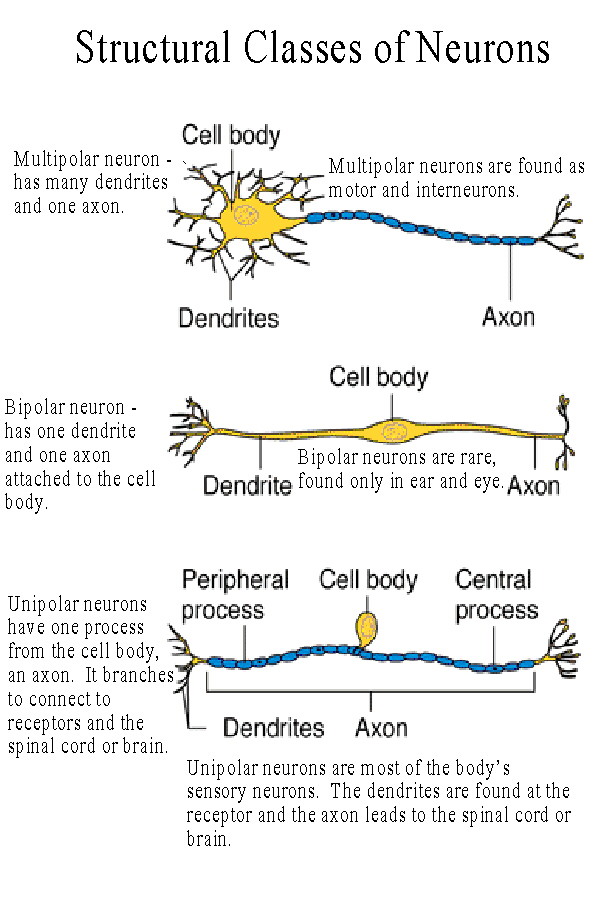
Neuron Structure And Classification
Sensory Neuron Wikipedia

Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neuron Byju S
Neuron Structure And Classification

Sensory Neuron Wikipedia

6 5 Nerves Hormones And Homeostasis Bioninja

What Is The Structure Of A Sensory Neuron Quora
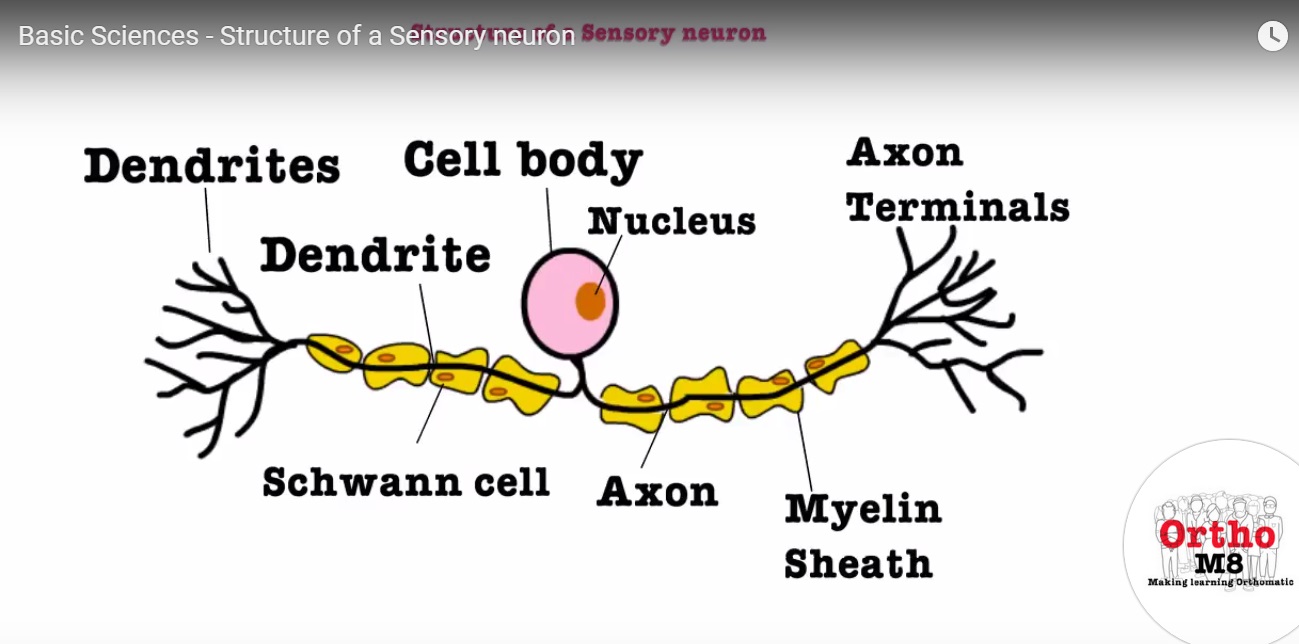
Structure Of A Sensory Neuron Orthopaedicprinciples Com
1
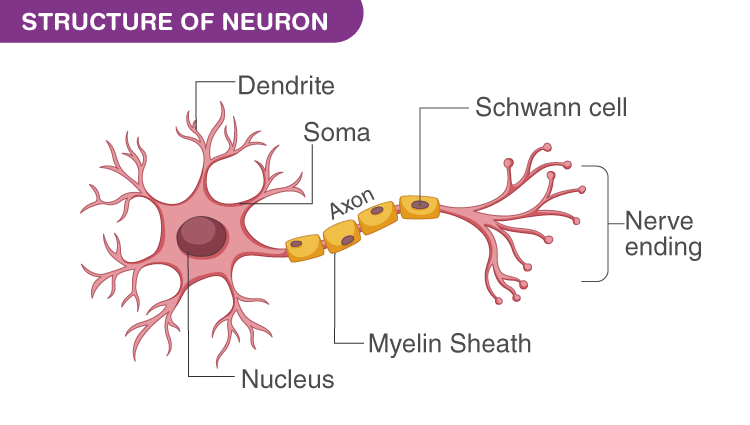
What Is A Neuron Definition Structure Parts And Function

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

What Is The Difference Between Sensory Neuron And A Motor Neuron Quora

Ch 11 Types Of Neurons

Anatomy Chapter 13 Peripheral Nervous System And Reflex Activity Studeersnel
Ppt Structure Function Information Processing Powerpoint Presentation Id
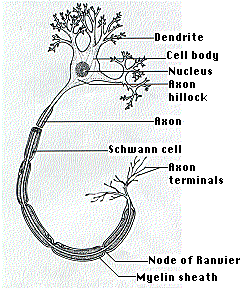
Neurons
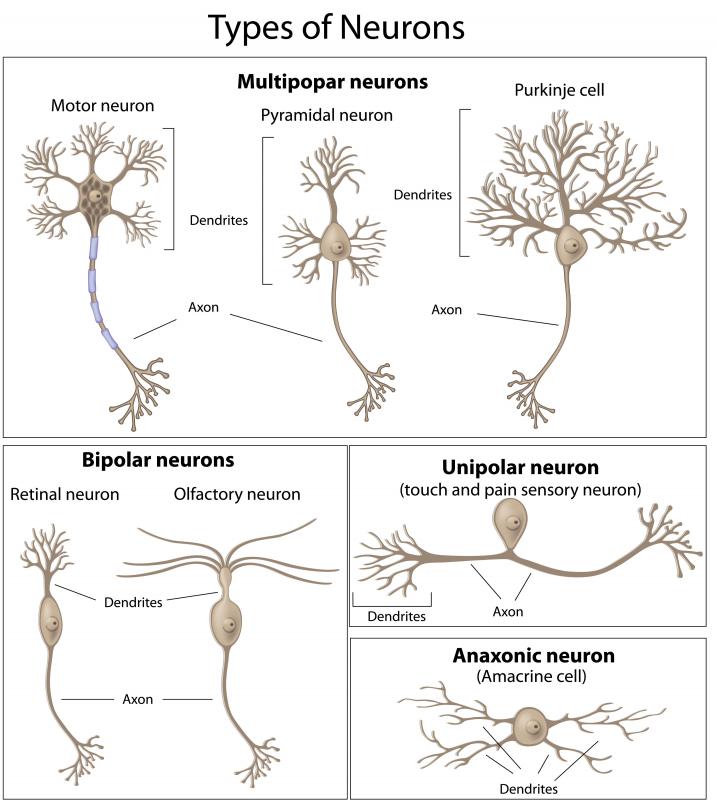
What Is The Function Of A Sensory Neuron With Pictures

Biopsychology Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Psychology Tutor2u

Diagram Of Sensory Neuron Car Fuse Box Wiring Diagram

Chapter 10
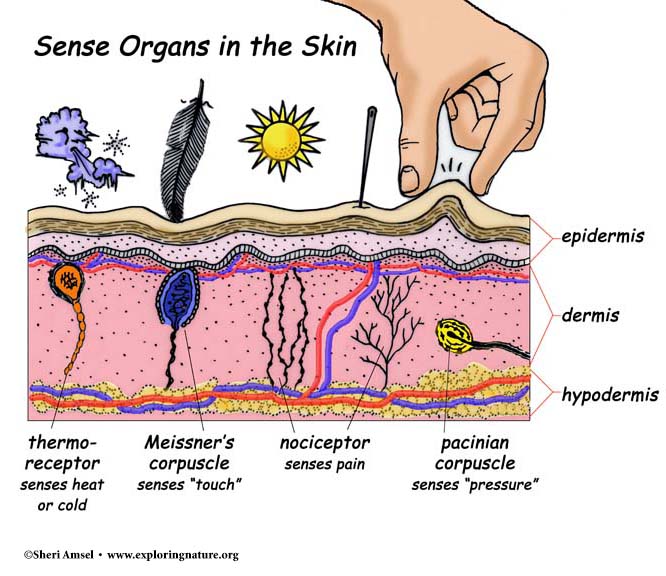
The Structures Locations And Functions Of The Sensory Receptors Earth S Lab

The Structure Of The Sensory Neuron Infographics Vector Illustration Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image

Chapter 10
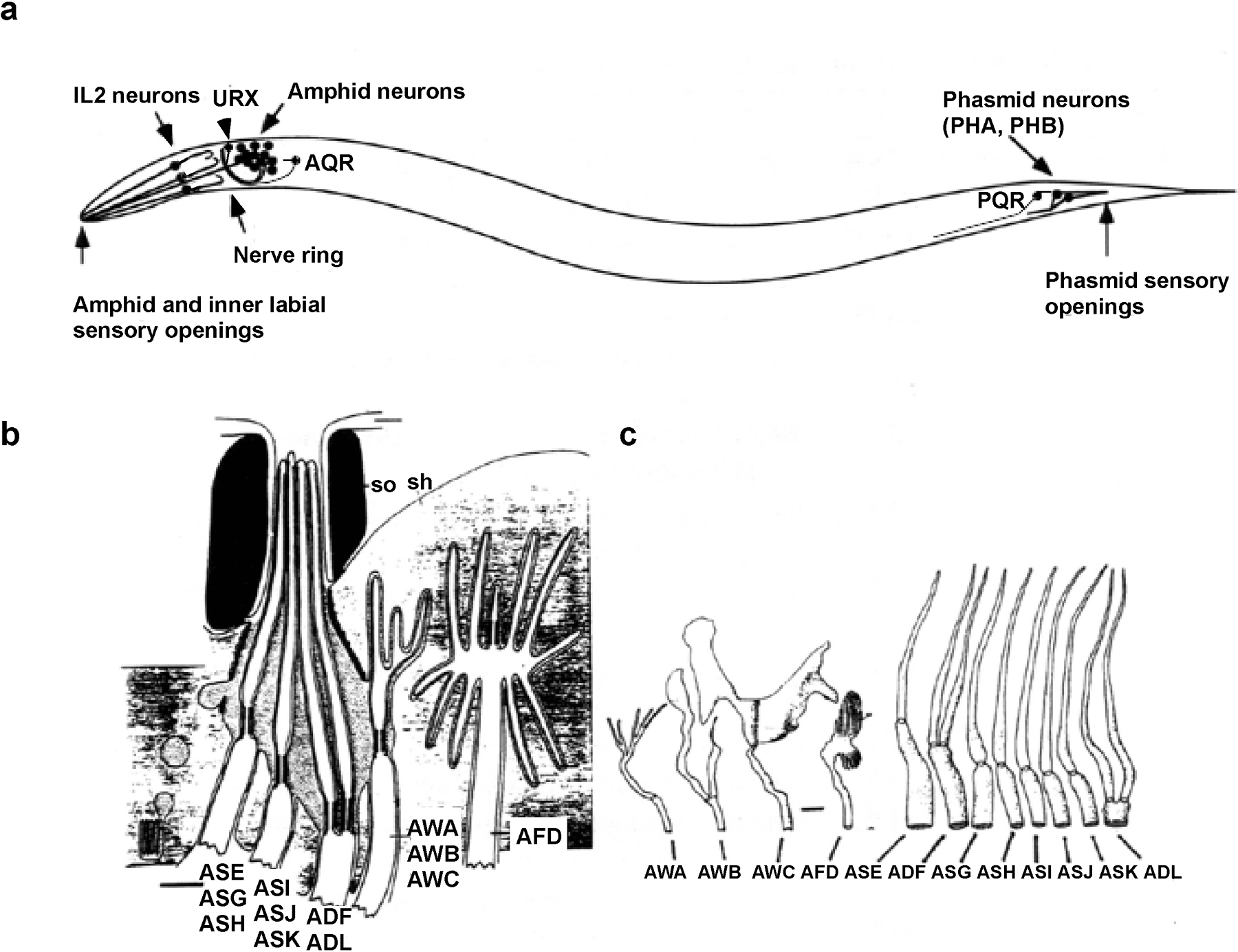
Chemosensation In C Elegans
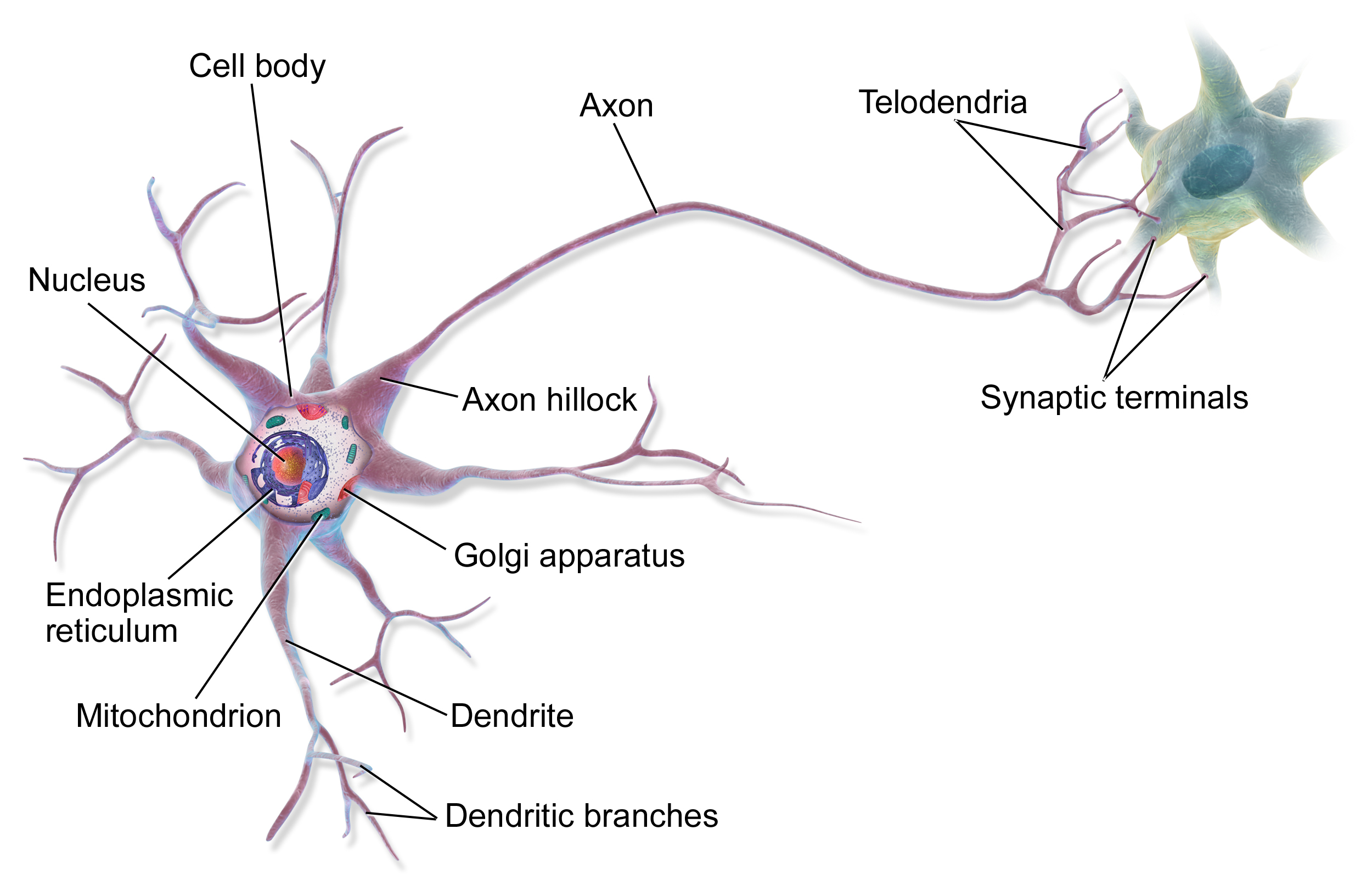
Neuron Wikipedia

Diabetic Neuropathy And The Sensory Neuron New Aspects Of Pathogenesis And Their Treatment Implications Kobayashi 18 Journal Of Diabetes Investigation Wiley Online Library

Types Of Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Astrocyte Pyromidal Betz Cell Microglia Set Infographics Vec In Types Of Neurons Neurons Neuron Structure

Structure Of Neurones
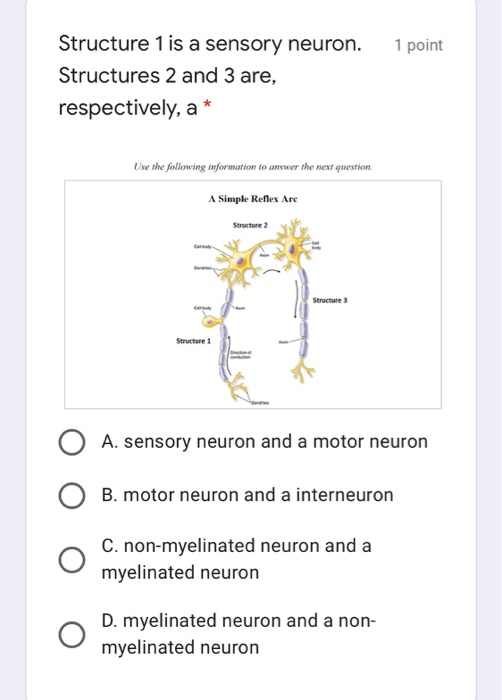
Solved 1 Point Structure 1 Is A Sensory Neuron Structure Chegg Com

Neuron Structure And Function Sensory Neurons Association Neurons Motor Neurons Youtube

Neurons Boundless Psychology

Nervous System Divisions Of The Nervous System Nervous Tissue

Types Of Neurons Sensory Afferent Motor Efferent More Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Structure Of A Neuron Unity Companies Rr School Of Nursing
The Central Nervous System Structure And Functions
Labelled Diagram Of Motor Neuron Trusted Wiring Diagrams
Solved Identify Which Structure On The Diagram Would Be F Chegg Com

Three Layers Of The Hierarchical Structure Of Neurons Integrating Download Scientific Diagram
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
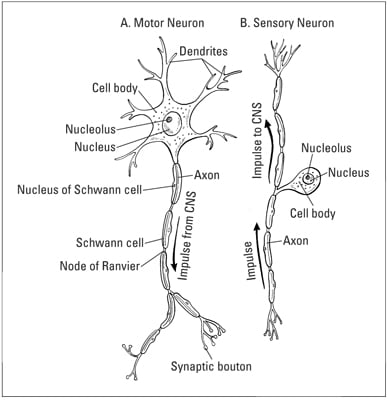
What S The Basic Structure Of Nerves Dummies
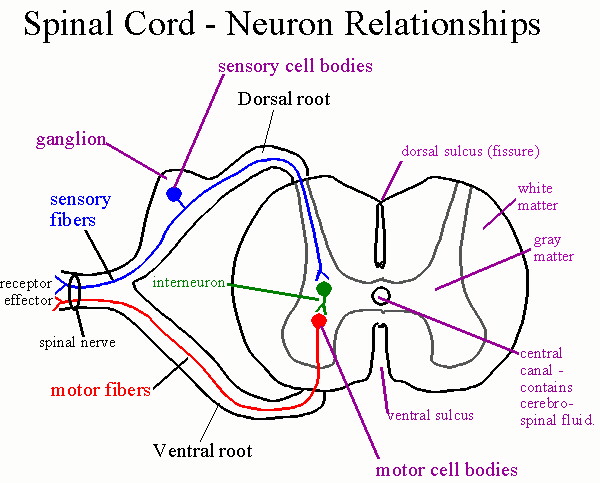
Biol 237 Class Notes The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves
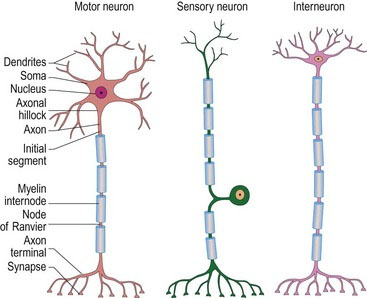
Neurohistology Physiology And Supporting Structures Veterian Key
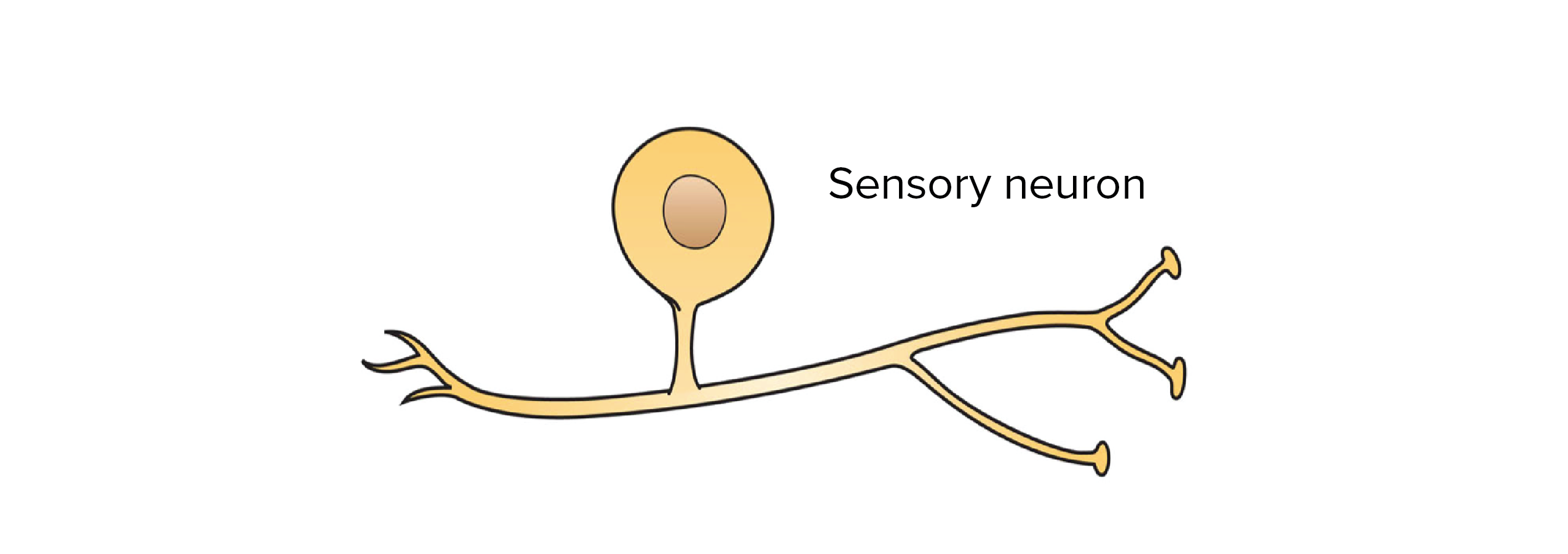
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Glial Ensheathment Of The Somatodendritic Compartment Regulates Sensory Neuron Structure And Activity Pnas

3 Structure Of Rod And Cone Photoreceptors Photoreceptors Are Polarized Download Scientific Diagram

Vagal Sensory Neuron Subtypes That Differentially Control Breathing Cell

Dcirl Reduces Camp Levels In Sensory Neurons In Response To Mechanical Download Scientific Diagram
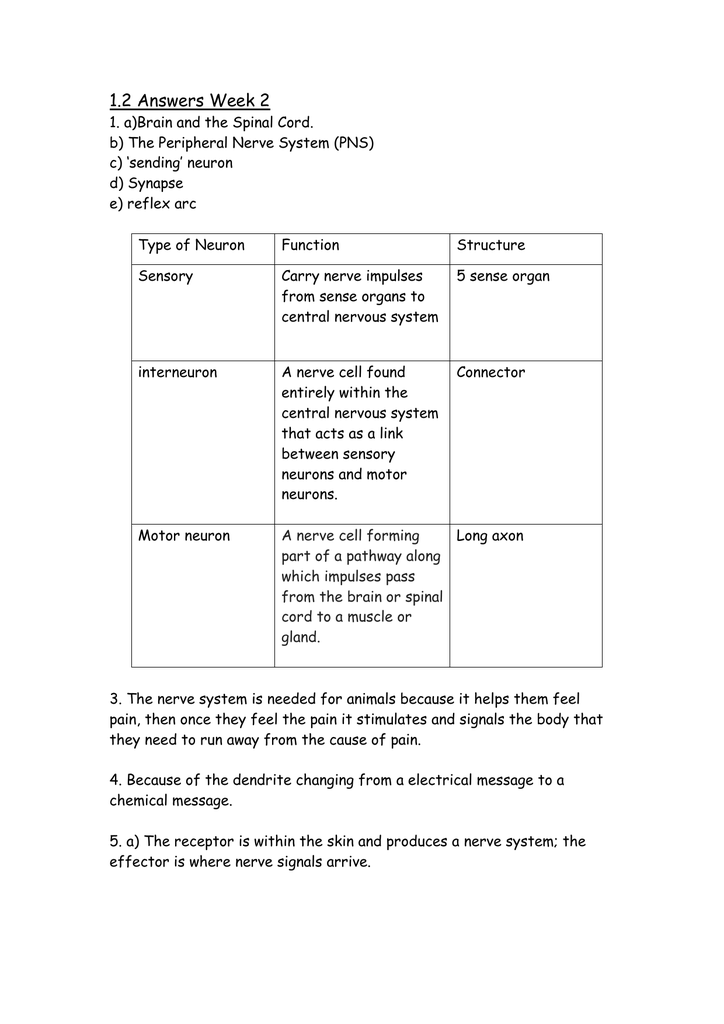
Week 2
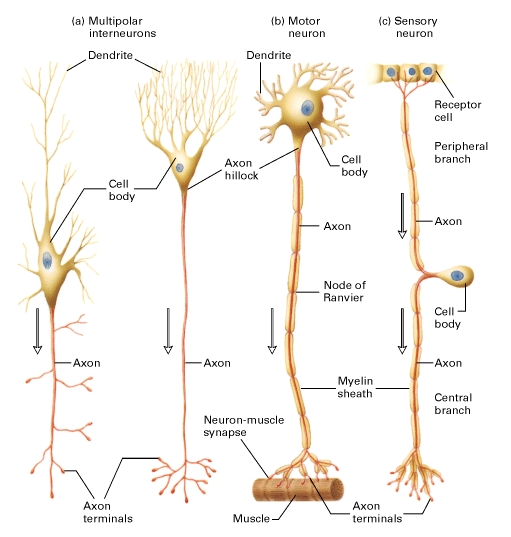
Human Physiology Structure And Function Of The Nervous System I Genius
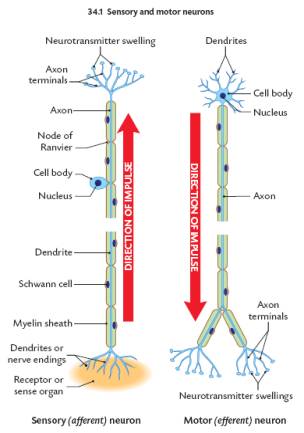
The Nervous System
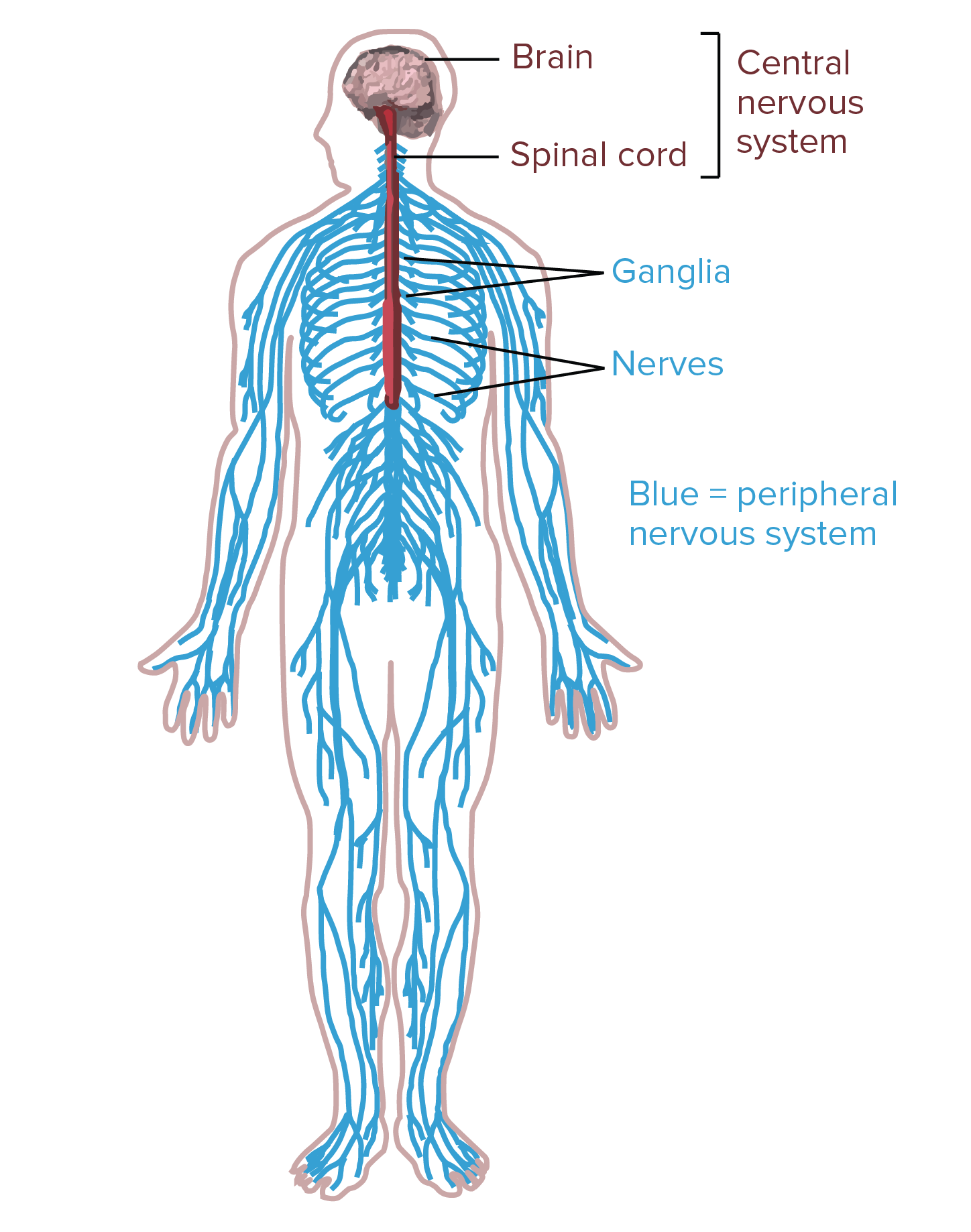
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
Structural Functional Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neuron Viva Differences

The Nervous System

Pin By Thyra H On Homeschooling Types Of Neurons Neurons Motor Neuron
The Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Psychology Hub

Neurons

Sensory Neuron An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Structure And Types Of Neuron The Nervous Tissue Online Science Notes

Neurones And Synapses Gcse Revision Biology Human Body Nervous System Neurones And Synapses Revision World

Human Physiology Neurons The Nervous System Ii

Histology 4000 Nervous System I Lecture Notes 7a

Difference Between Afferent And Efferent Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Stimulus Response Bioninja
Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neurons Definition Structure Function Characteristics
Seer Training Nerve Tissue

View Image
Neuron Structure And Classification Brooke Hamilton Neural Tissue



