Structure Of Sensory And Motor Neurons

Sensory Somatic Nervous System Biology For Majors Ii

14 5 Sensory And Motor Pathways Anatomy Physiology

Diagram Of Sensory Neuron Car Fuse Box Wiring Diagram
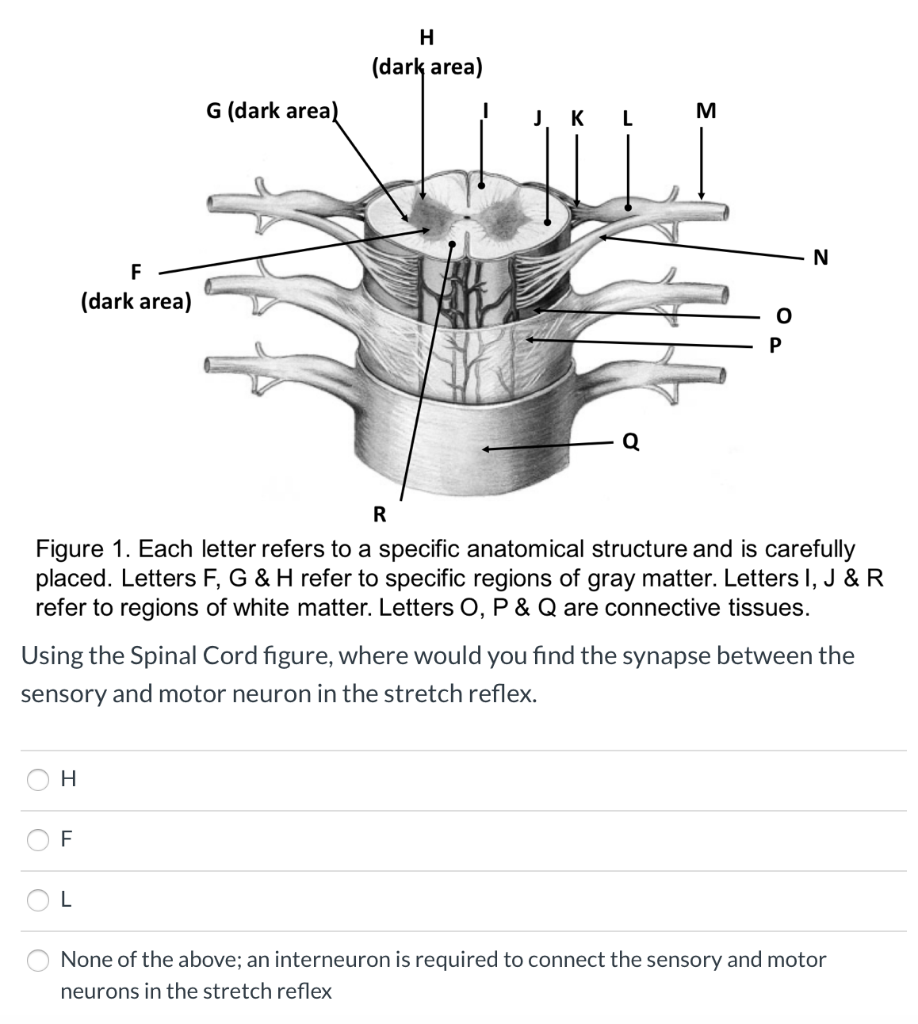
Solved Question One Using The Spinal Cord Figure Where Chegg Com

Afferent Nerve Fiber Wikipedia

Sensory Neuron An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Upper motor neuron lesions can involve the motor cortex, the internal capsule, the spinal cord, and other structures of the brain through which the corticospinal tract descends If the upper motor neurons are damaged or destroyed, as frequently occurs with stroke or spinal cord injury, paralysis (loss of voluntary movement) results.
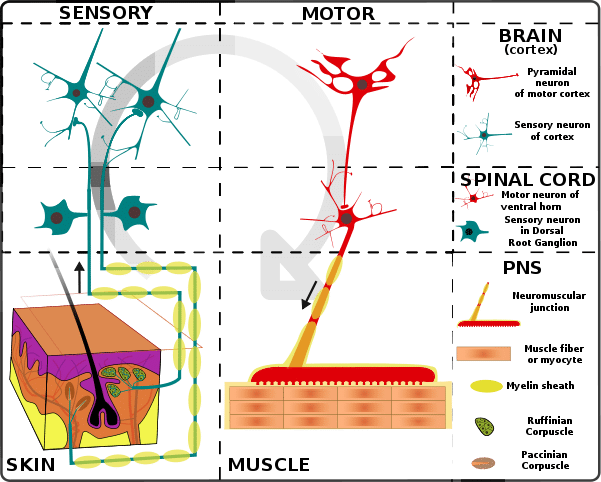
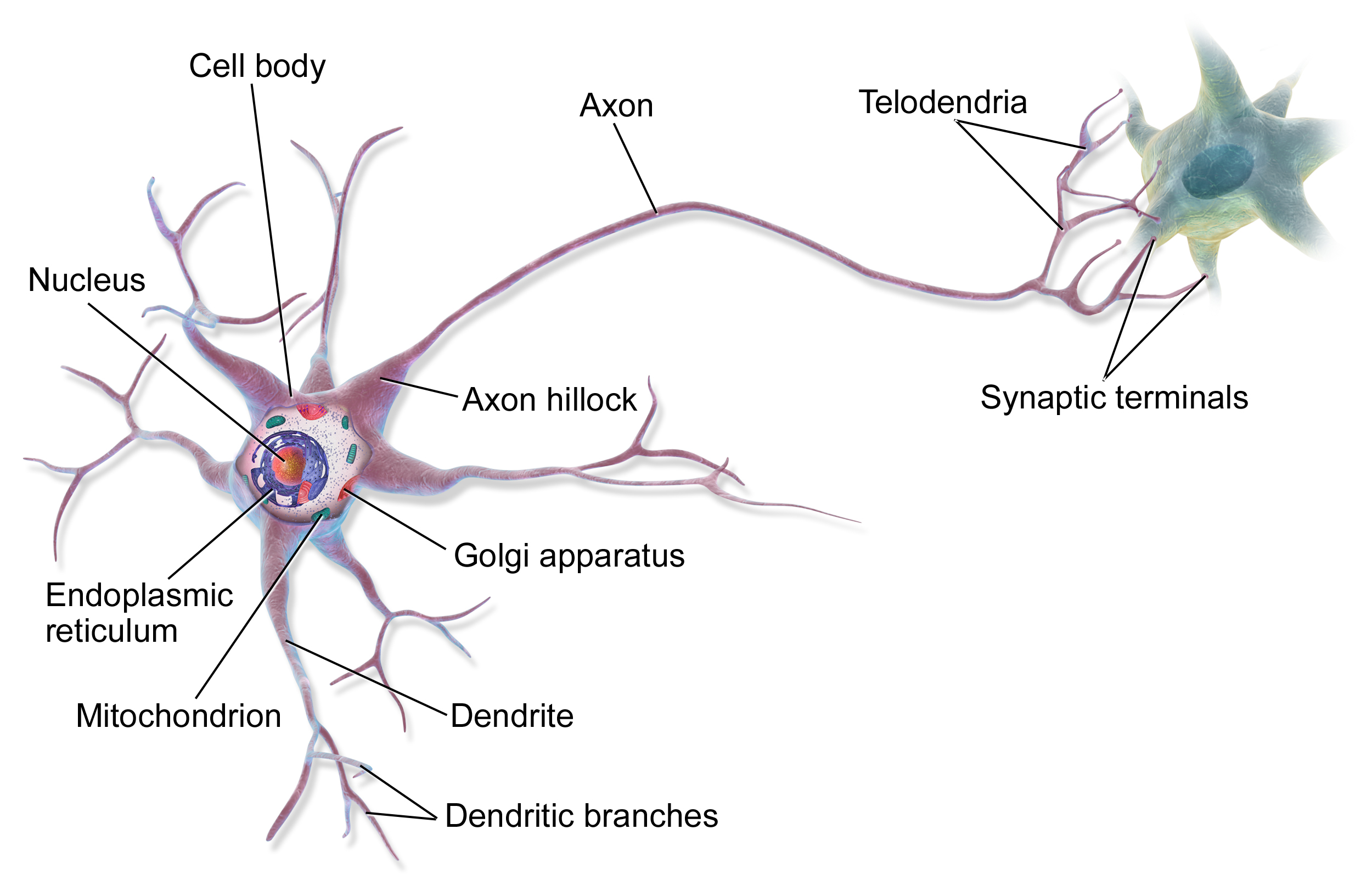
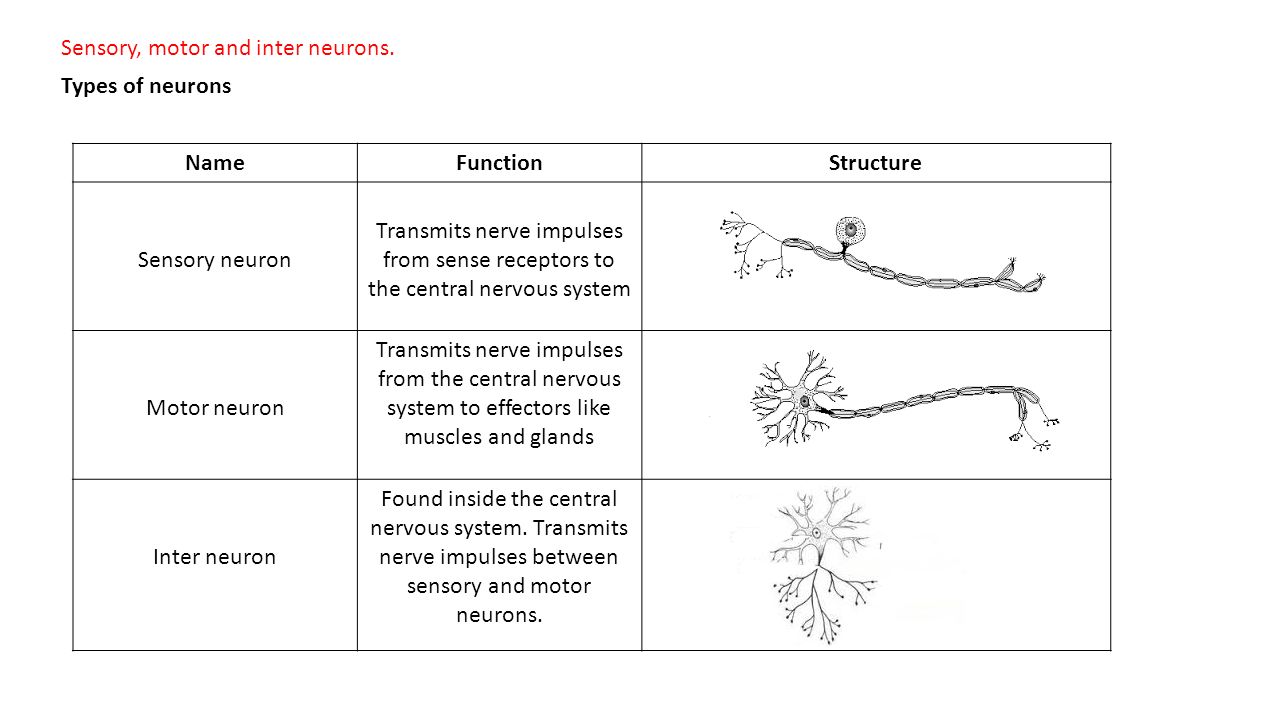
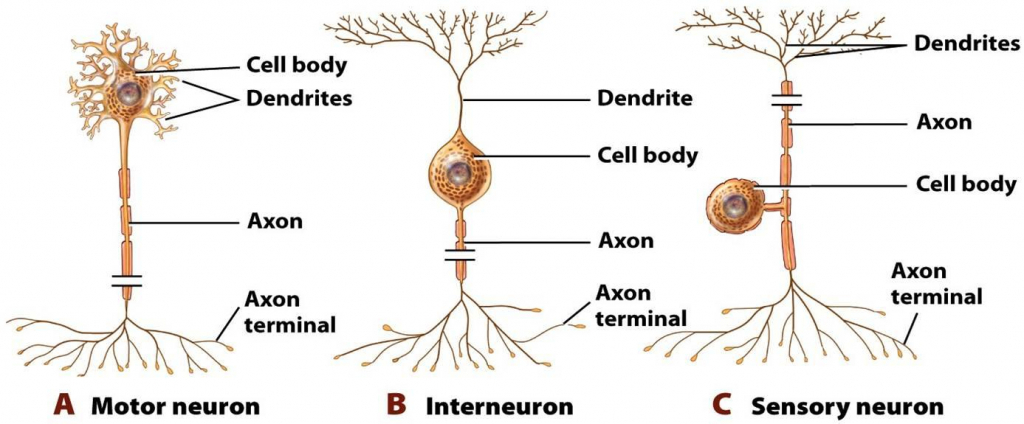
Structure of sensory and motor neurons. Definition A sensory neuron (sometimes referred to as an afferent neuron) is a nerve cell that detects and responds to external signals Sensory neurons receive information via their receptors, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, and convert this information into electrical impulsesThese impulses act as signals and are passed on to the central nervous system. A motor homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to motor processing for different anatomical divisions of the body The primary motor cortex is located in the precentral gyrus, and handles signals coming from the premotor area of the frontal lobes A sensory homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to sensory processing for different anatomical divisions of the body. Motor neurons that regulate muscle contractions have a cell body on one point, a long axon in the middle and dendrites on the other point Sensory neurons have dendrites on both ends, connected with a long axon with a cell body in the middle Interneurons, or associative neurons, bring information between motor and sensory neurons.
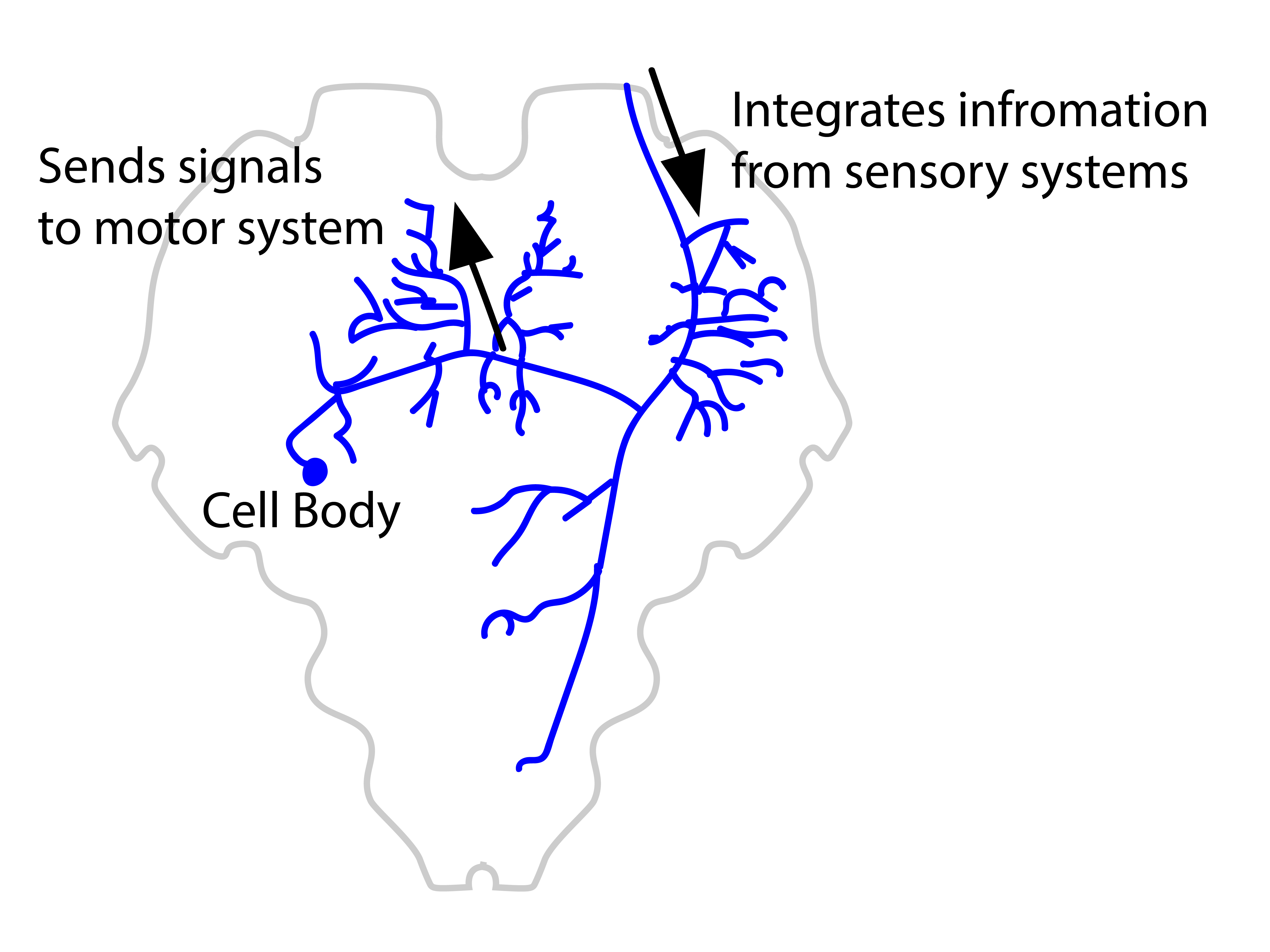
There are three primary types of neuron sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons Structures of a Neuron In addition to having all the normal components of a cell (nucleus, organelles, etc) neurons also contain unique structures for receiving and sending the electrical signals that make neuronal communication possible. As the name suggests, sensory neurons are associated with the conduction of sensory impulses Motor neurons conduct signals from the CNS to the glands and skeletal muscle of the body Interneurons are also called relay neurons and are found exclus. Relay neurones (also called interneurons) – between sensory and motor neurones Relay neurons carry messages around the CNS (Central Nervous System) and connect between sensory neurones and motor neurones A relay (relay neurone) runner ran between Sensory Man (sensory neurone) and the motor (motor neurone).
Efferent Neurons are motor neurons Explain how all three neurons work together to perform a 'reflex action' with the example of Ariana holding a hot mug The receptor cells in Ariana's hand would be sent to the sensory neurons which would relay that information to the interneurons in the CNS specifically the spinal cord. Sensory Neurons are also known as AFFERENT Neurons and Motor Neurons are also known as EFFERENT Neurons 25 Finally, we have the Interneurons that connect the Sensory Neurons and the Motor Neurons for facilitating transmission of information or signals These Interneurons are located entirely inside the Central Nervous System. (motor neurons and interneurons or association neurons are multipolar neurons and compose most of the CNS neurons bipolar neurons have 2 processes 1 dendrite, and 1 axon on either side of the cell body & are found in the special senses like the retina of the eye, the olfactory cells of the nose, and the inner ear.
°Sensory receptors respond to stimuli and produce action potentials in sensory neurons ° Sensory neurons propagate action potentials to the CNS ° Interneurons in the CNS synapse with sensory neurons and with motor neurons ° Motor neurons carry action potentials from the CNS to effector organs ° Effector organs, such as muscles or. The nervous system has three main functions sensory input, integration of data and motor output Sensory input is when the body gathers information or data, by way of neurons, glia and synapses The nervous system is composed of excitable nerve cells (neurons) and synapses that form between the neurons and connect them to centers throughout. The dorsal root contains only the axons of sensory neurons, whereas the ventral roots contain only the axons of the motor neurons Some of the branches will synapse with local neurons in the dorsal root ganglion, posterior (dorsal) horn, or even the anterior (ventral) horn, at the level of the spinal cord where they enter.
Neurons are classified into three major classes based on their functions;. Motor neurons, on the other hand, are responsible for responding to the commands made by the brain upon delivering sensory information In neurobiology, one of the important principles on which the human sensory and motor systems are based is known as the sensory pathways principle. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters) Check Point g Humans have three types of neurones Sensory neurones have long axons and transmit nerve impulses from sensory receptors all over the body to the central nervous system.
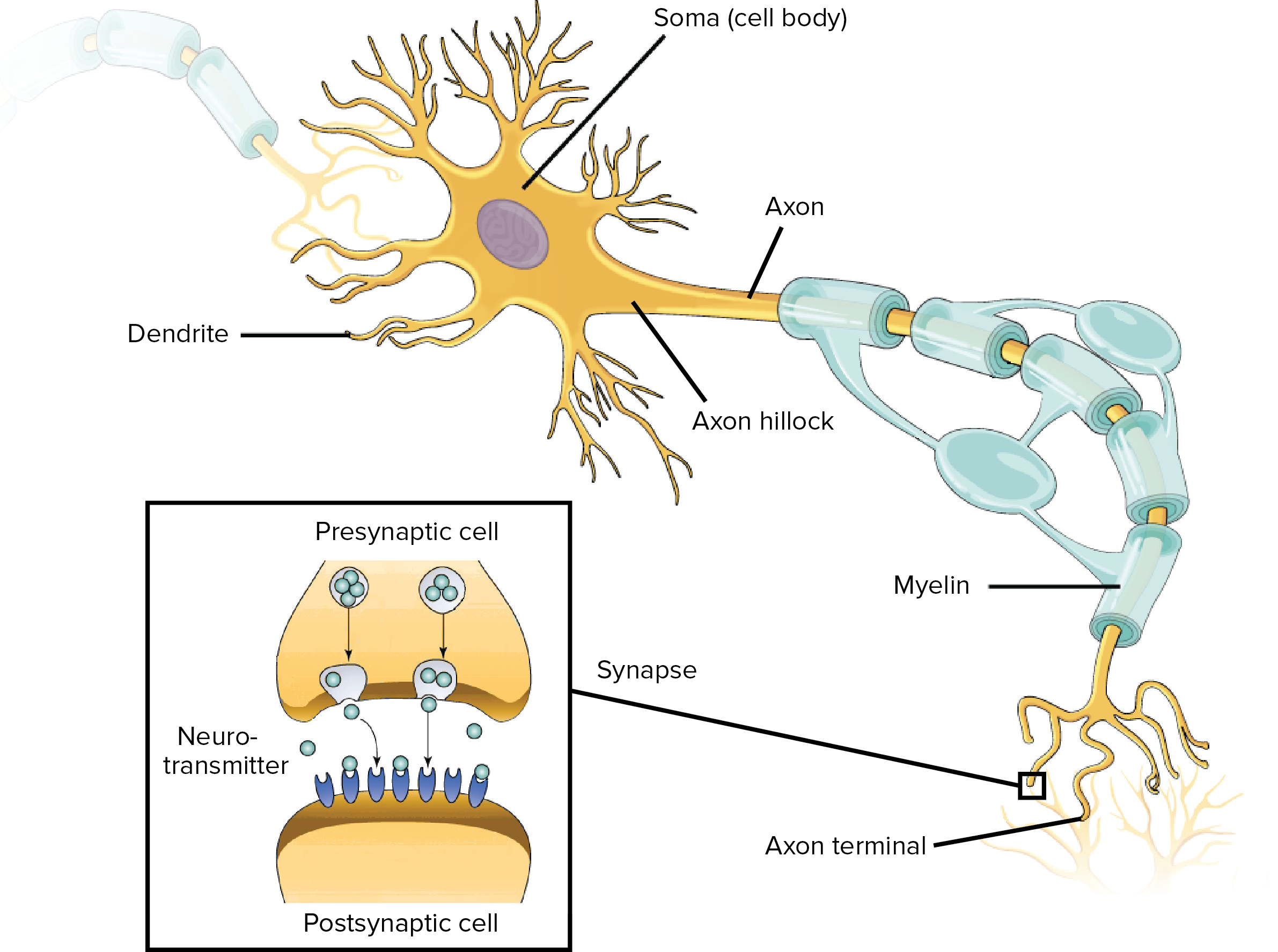
Structure and functions of neurons STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by BHC_XBLADE Terms in this set (14) Go through the mem technique SMARTER Sensory neurons Motor neurons Axon Relay neurons Terminal buttons Electrical transmission/action potential Reflex arc. The basic functions of a neuron Receive signals (or information) Integrate incoming signals (to determine whether or not the information should be passed along) Communicate signals to target cells (other neurons or muscles or glands). As well as transferring signals between sensory and motor neurons, interneurons can also communicate with each other, forming circuits of various complexity They are multipolar, just like motor neurons Neurons in the brain In the brain, the distinction between types of neurons is much more complex Whereas in the spinal cord we could easily.
Interneurons, sensory neurons, and motor neurons Motor neurons are the component of the peripheral nervous system that functions to carry the nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral body parts Some structural variations so exist among these. Neurons can also be classified by the direction that they send information Sensory (or afferent) neurons send information from sensory receptors (eg, in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system Motor (or efferent) neurons send information AWAY from the central nervous system to muscles or glands. Interneurons, sensory neurons, and motor neurons Motor neurons are the component of the peripheral nervous system that functions to carry the nerve impulses from the central nervous system to the peripheral body parts Some structural variations so exist among these.
Eg neurons of dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord Bipolar neuron In such neurons, two processes, one dendrite and one axon, arise from the cell body Eg neurons of retina and internal ear Multipolar neuron Such neurons have one axon and two or more dendrites More than 99% of the neurons are multipolar type. These neurons are also known as pseudo unipolar neurons Structure of Motor Neurons To understand the difference between sensory neuron and motor neuron in a better way, let's learn the structure of Motor neurons Image will be Uploaded Soon Motor nerves transmit the signals from the CNS to the sensory organs and thus, help in initiating. A motor homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to motor processing for different anatomical divisions of the body The primary motor cortex is located in the precentral gyrus, and handles signals coming from the premotor area of the frontal lobes A sensory homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to sensory processing for different anatomical divisions of the body.
Neurons are classified into three major classes based on their functions;. Motor neurons are effect neurons whose function is to carry signals out of the central nervous system to target effector organs such as muscles and glands Their structure is characterized by short dendrites and long axons allowing them to extend far distances across the body in order to provoke responses. A motor homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to motor processing for different anatomical divisions of the body The primary motor cortex is located in the precentral gyrus, and handles signals coming from the premotor area of the frontal lobes A sensory homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to sensory processing for different anatomical divisions of the body.
The dorsal root contains only the axons of sensory neurons, whereas the ventral roots contain only the axons of the motor neurons Some of the branches will synapse with local neurons in the dorsal root ganglion, posterior (dorsal) horn, or even the anterior (ventral) horn, at the level of the spinal cord where they enter. Motor neurons are effect neurons whose function is to carry signals out of the central nervous system to target effector organs such as muscles and glands Their structure is characterized by short dendrites and long axons allowing them to extend far distances across the body in order to provoke responses. Being the most basic units of the human nervous system, neurons play a vital role in sensing and responding to different external as well as internal stimuli A motor neuron is one of the three types of neurons involved in this process Read about the structure and function of a motor neuron with reference to a neatly labeled diagram, in this Bodytomy post.
Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron Neurons that carry sensory impulse from sensory organs to the central nervous system are known as sensory neurons A neuron that carries motor impulses from the central nervous system to specific effectors is known as motor neurons They are located in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal nerve. The Structure and Function of Sensory, Relay and Motor Neurons The nervous system is composed of specialised cells called neurons The neurons form pathways in the brain and throughout the body by being connected to one another by synapses There are about 100 billion neurons or nerve cells in the average nervous system. Sensory Neuron Motor Neuron Neurons that carry sensory impulse from sensory organs to the central nervous system are known as sensory neurons A neuron that carries motor impulses from the central nervous system to specific effectors is known as motor neurons They are located in the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal nerve.
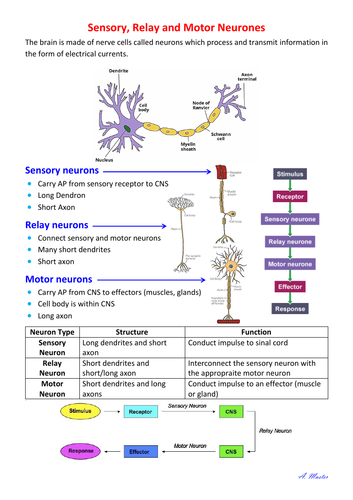
This process is coordinated by the sensory neurons, which are situated along the nerve conducting pathway Motor Nerves Motor nerves connect the central nervous system and muscles in the body, through the motor neurons, where the motor nerves are originated The cell body for each nerve lies in the spinal cord. Types of Neurons sensory, intereuron, motor # Description A neuron, also known as a neurone and nerve cell, is an electrically excitable cell that receives, processes, and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. Motor neurons have a cell body, short dendrites and a long axon Their function is to conduct impulses to an effector (muscle or gland)Sensory neurons, on the other hand, have a cell body, long dendrites and a short axon Their function is to conduct impulses to the Central Nervous System.
Let’s begin with the definition of a motor neuron A motor neuron is basically a nerve cell whose function is to respond to sensory stimulation by producing the required muscular movement Motor neurons are located in the spinal cord, and their axon protrudes outside to the muscle fibers. The motor part of the spindle is provided by motor neurons up to a dozen gamma motor neurons and one or two beta motor neurons, collectively called fusimotor neurons citation needed These activate the muscle fibres within the spindle Gamma motor neurons supply only muscle fibres within the spindle, whereas beta motor neurons supply muscle. Upper motor neuron lesions can involve the motor cortex, the internal capsule, the spinal cord, and other structures of the brain through which the corticospinal tract descends If the upper motor neurons are damaged or destroyed, as frequently occurs with stroke or spinal cord injury, paralysis (loss of voluntary movement) results.
For example, some sensory neurons respond to tactile stimuli and can activate motor neurons in order to achieve muscle contraction Such connections between sensory and motor neurons underlie. To understand the difference between sensory nerve and motor nerve, it is important that we. Motor neurons (MNs) are neuronal cells located in the central nervous system (CNS) controlling a variety of downstream targets This function infers the existence of MN subtypes matching the identity of the targets they innervate To illustrate the mechanism involved in the generation of cellular diversity and the acquisition of specific identity, this review will focus on spinal MNs (SpMNs.
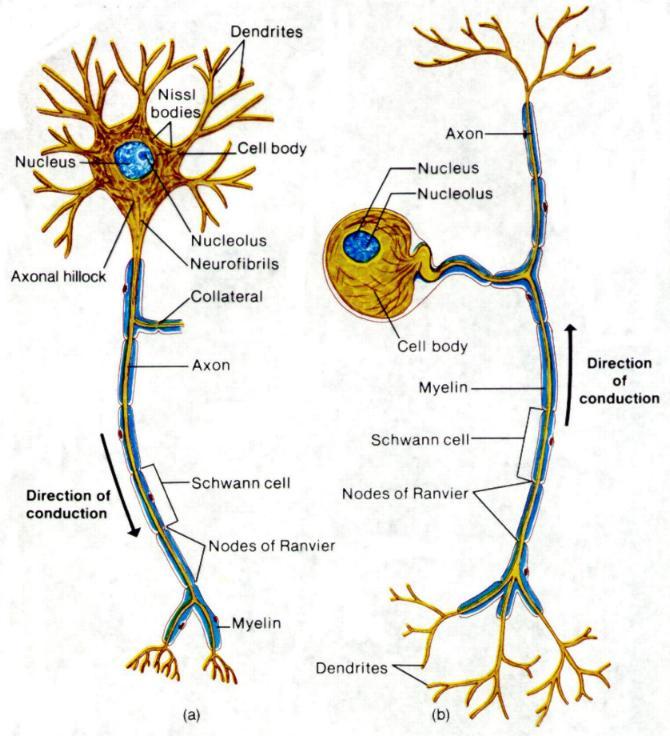
Unipolar neurons are found primarily in the afferent division of the PNS Functional Classification of Neurons Neurons are classified functionally according to the direction in which the signal travels, in relation to the CNS This classification also results in three different types of neurons sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. As well as transferring signals between sensory and motor neurons, interneurons can also communicate with each other, forming circuits of various complexity They are multipolar, just like motor neurons Neurons in the brain In the brain, the distinction between types of neurons is much more complex Whereas in the spinal cord we could easily. As you can see from the diagram, the motor and sensory neurons have the same basic architecture, but do necessarily have differences in structure The axon transmits electrochemical stimuli away from the cell body In somatic motor neurons, it.
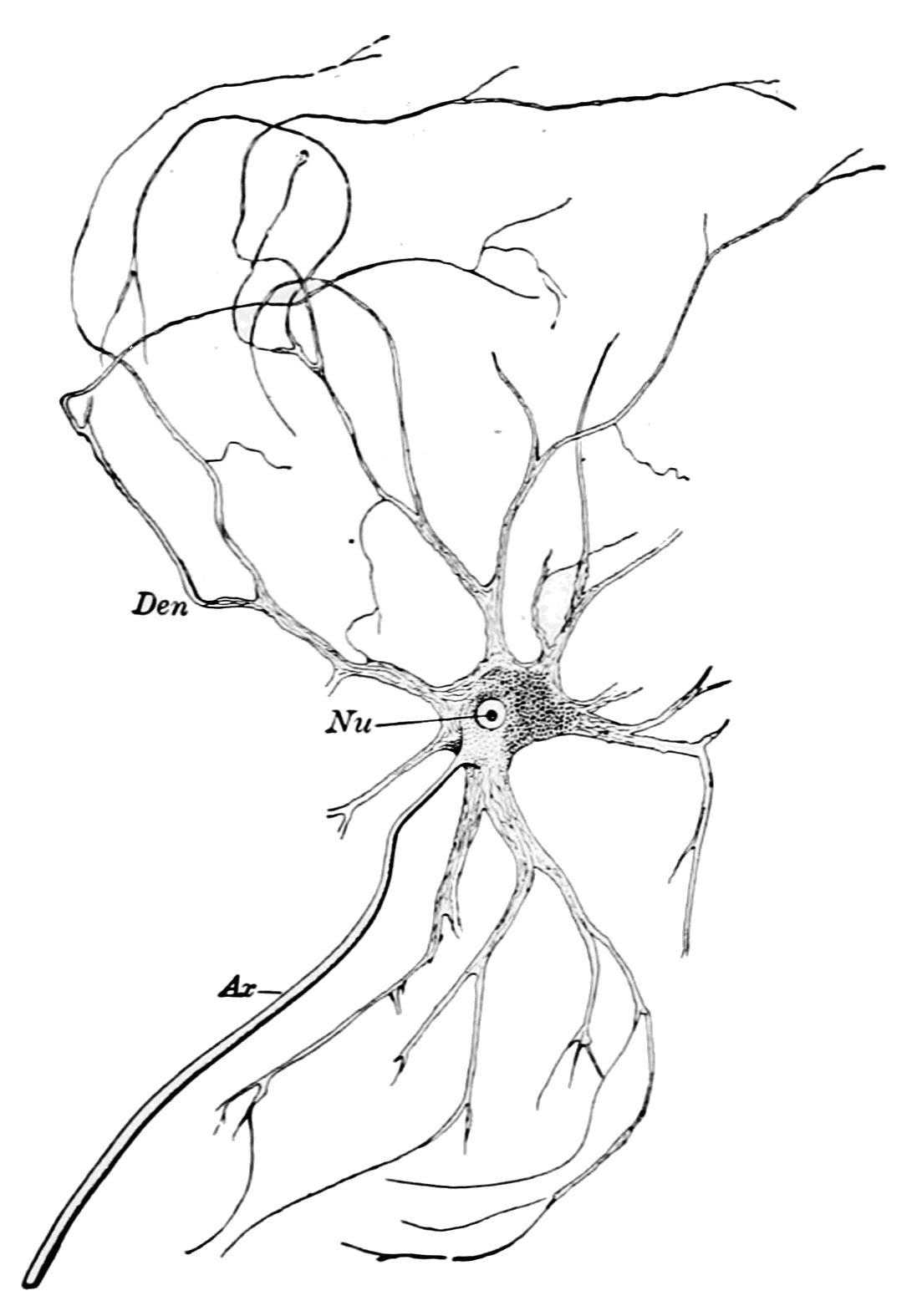
Motor neurons carry motor impulses from the central nervous system to specific effectors. These neurons are usually concentrated in areas called ganglia and their dendrite branches extend to the skin or to sensory organs and act as sensory receptors (either directly or indirectly) 11 Motor neurons or Efferent neurons – These neurons carry impulses AWAY from the cell body and thus the central nervous system to muscles, gland, or. Neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location However, nearly all neurons have three essential parts a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
Relay neurones (also called interneurons) – between sensory and motor neurones Relay neurons carry messages around the CNS (Central Nervous System) and connect between sensory neurones and motor neurones A relay (relay neurone) runner ran between Sensory Man (sensory neurone) and the motor (motor neurone). A motor homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to motor processing for different anatomical divisions of the body The primary motor cortex is located in the precentral gyrus, and handles signals coming from the premotor area of the frontal lobes A sensory homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to sensory processing for different anatomical divisions of the body. These neurons are usually concentrated in areas called ganglia and their dendrite branches extend to the skin or to sensory organs and act as sensory receptors (either directly or indirectly) 11 Motor neurons or Efferent neurons – These neurons carry impulses AWAY from the cell body and thus the central nervous system to muscles, gland, or.
Efferent neurons carry impulses from the central nervous system to other parts of the body and most notably include motor neurons A sensory neuron generally transmits its information toward the central nervous system, which is primarily contained in the brain and in parts of the spineSensory input, then, is received by the dendrites of the nerve cell and sent through the axon until it either. Relay neurons are found in the brain and spinal cord and allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate Motor neurons are found in the central nervous system (CNS) and control muscle movements When motor neurons are stimulated they release neurotransmitters that bind to the receptors on muscles to trigger a response, which lead to movement As you can see from the diagrams above, all three neurons consist of similar parts The dendrites receive signals from other neurons or from sensory. There are three primary types of neuron sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons Structures of a Neuron In addition to having all the normal components of a cell (nucleus, organelles, etc) neurons also contain unique structures for receiving and sending the electrical signals that make neuronal communication possible.
View Nervous_System_I10ppt from BIOL 2340 at University of Mary HardinBaylor Nervous System Structure and Function Functions Sensory input Integration Motor output Classification Central. On the basis of function neurons are mainly two types 1 Sensory neuron and 2 Motor neuronInterneurons are also included in this type STRUCTURE OF A TYPICAL NEURON A typical neuron primarily consist of the Cell body and processes, also called neurites Neurites are two types – A Dendrites and B Axon. Sensory and motor neurons are two types of neurons They carry nerve impulses to and from the central nervous system Sensory and motor neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites and axon The action potential travels across these neurons.
Motor neurons, on the other hand, are responsible for responding to the commands made by the brain upon delivering sensory information In neurobiology, one of the important principles on which the human sensory and motor systems are based is known as the sensory pathways principle. Types of Neurons Sensory Neurons Transmit impulses from a sensory receptor cell to a relay or motor neuron Relay Neurons Transmit impulses between neurons Can have many short axons and dendrons Motor Neurons Transmit impulses from a relay neuron or sensory neuron to an effector cell such as a muscle or gland. With the methods used in far from onset preHD sensorymotor neural macro or microstructure and brain function were similar to healthy controls This suggests that any observable structural and functional change in preHD nearer to onset, or in manifest HD, at least using comparable techniques such as in this study, most likely reflects an.
°Sensory receptors respond to stimuli and produce action potentials in sensory neurons ° Sensory neurons propagate action potentials to the CNS ° Interneurons in the CNS synapse with sensory neurons and with motor neurons ° Motor neurons carry action potentials from the CNS to effector organs ° Effector organs, such as muscles or. °Sensory receptors respond to stimuli and produce action potentials in sensory neurons ° Sensory neurons propagate action potentials to the CNS ° Interneurons in the CNS synapse with sensory neurons and with motor neurons ° Motor neurons carry action potentials from the CNS to effector organs ° Effector organs, such as muscles or. Motor neurons that regulate muscle contractions have a cell body on one point, a long axon in the middle and dendrites on the other point Sensory neurons have dendrites on both ends, connected with a long axon with a cell body in the middle Interneurons, or associative neurons, bring information between motor and sensory neurons.
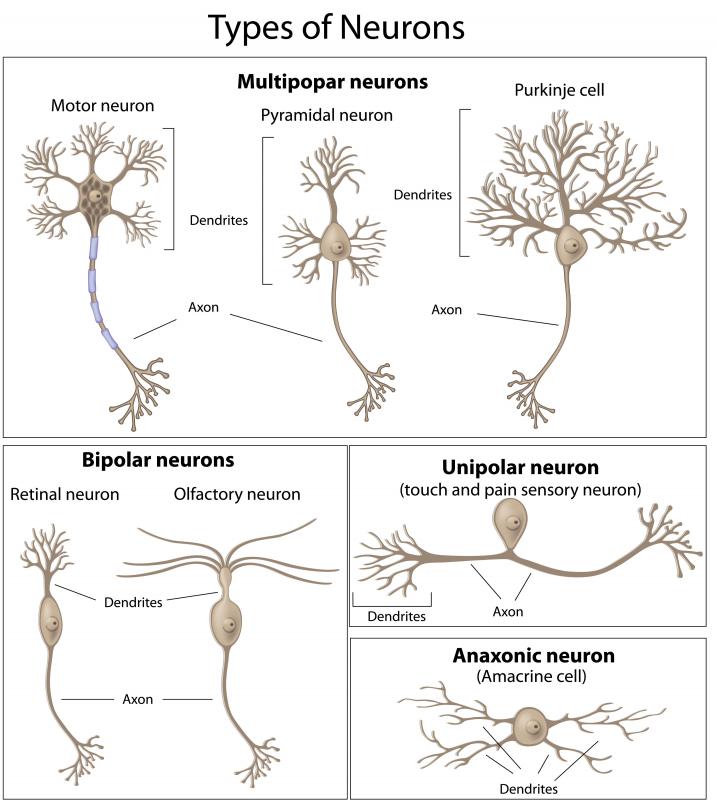
What Is The Function Of A Motor Neuron With Pictures

Nerves Hormones And Homeostasis
Q Tbn And9gcq7aaf8bmfhts9odkda1mwuxgeglnu5evwitukmyrprmtutfbak Usqp Cau

Neurons
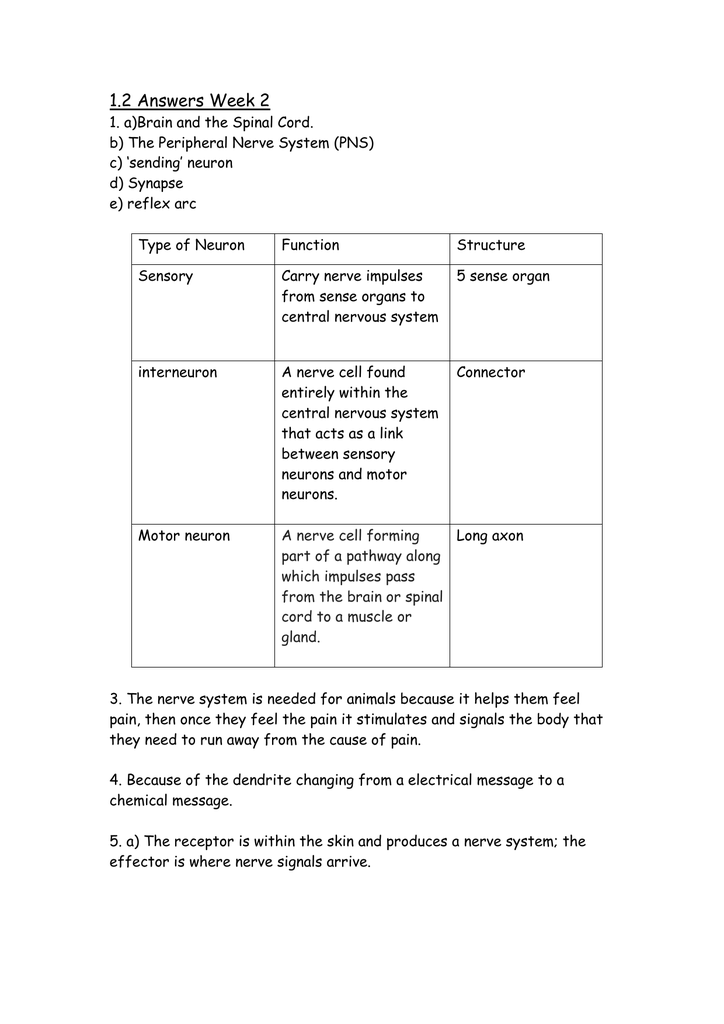
Week 2

14 5 Sensory And Motor Pathways Anatomy Physiology
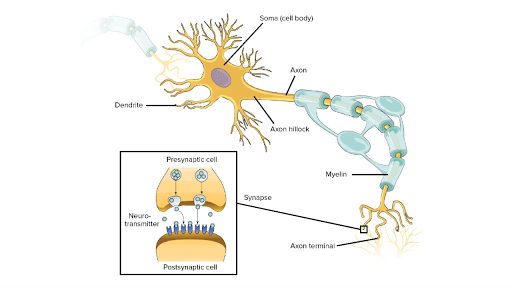
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Learn Types Of Neurons On The Basis Of Function In 4 Minutes

Somatic Nervous System Wikipedia

Nervous System Divisions Of The Nervous System Nervous Tissue

The Nervous System

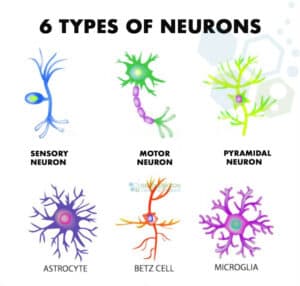
Types Of Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Astrocyte Pyromidal Betz Cell Microglia Set Infographics Vec In Types Of Neurons Neurons Neuron Structure

Topological Structure For A Dual Sensory Model For Food Attraction Download Scientific Diagram

Peripheral Nervous System Structure Summary Teachmephys

Sensory Neuron An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Classification Of Neurons

Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neurons Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
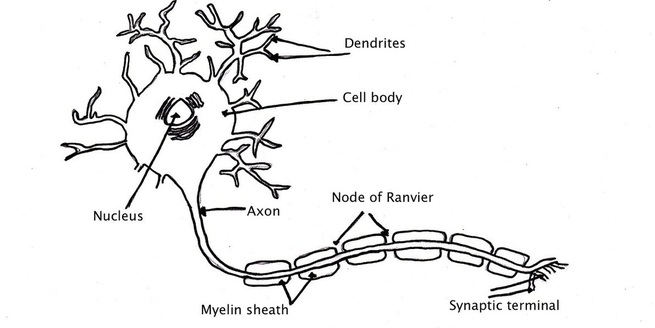
6 5 Nerves Hormones And Homeostasis Biology4ibdp
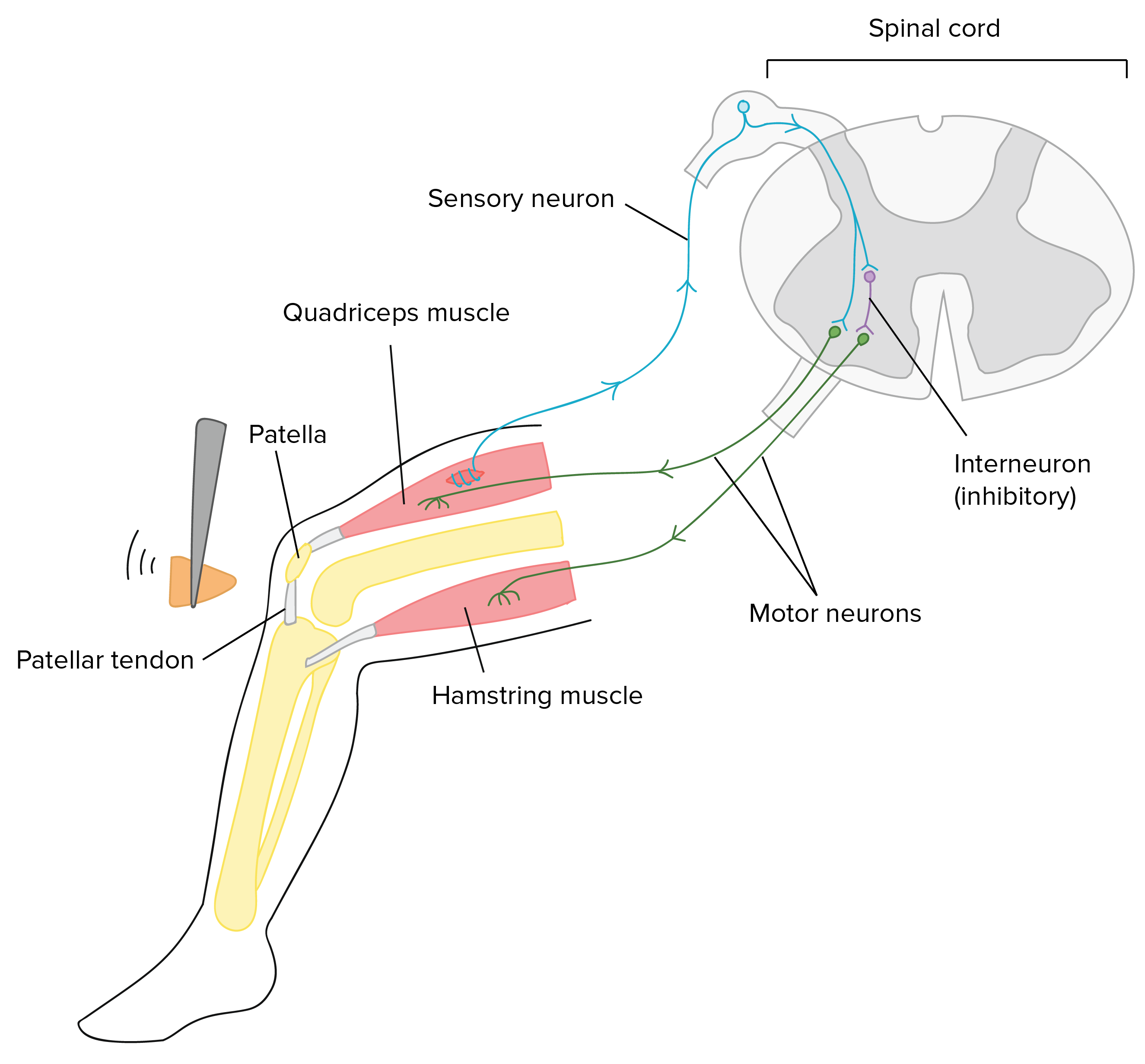
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Toxtutor Neurotoxicity

Pin By Thyra H On Homeschooling Types Of Neurons Neurons Motor Neuron

Biopsychology Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Psychology Tutor2u

Motor Neurones Sensory Neurones And Relay Neurones
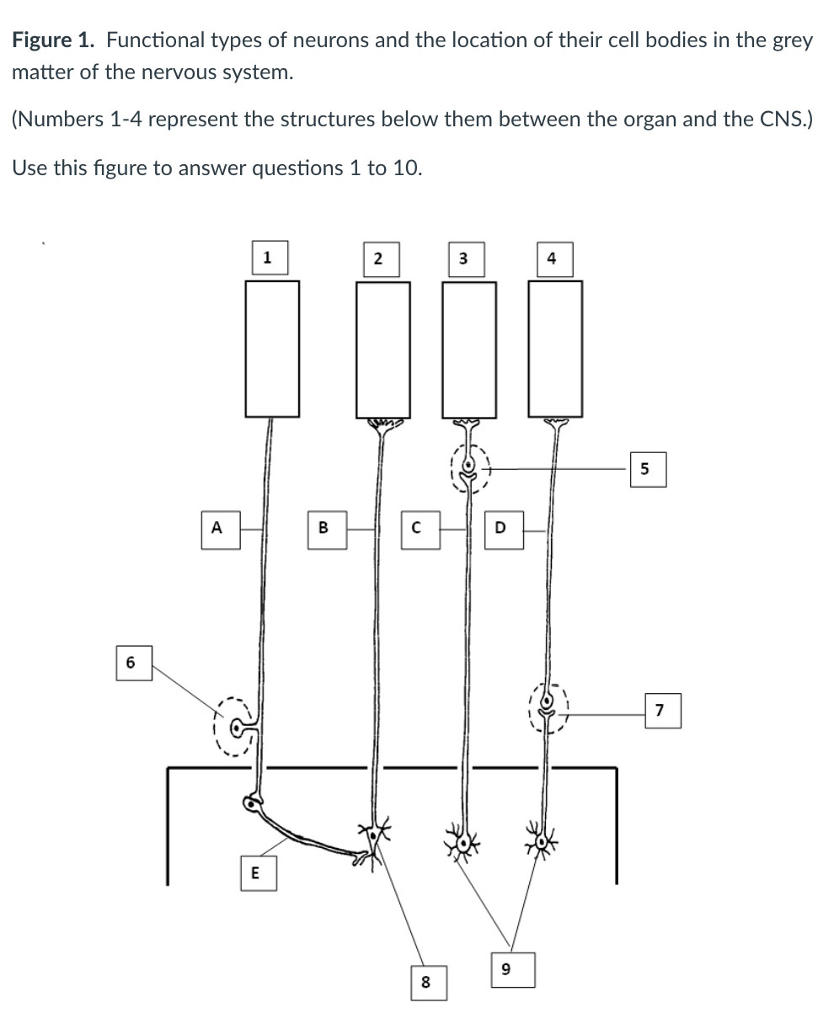
Solved Identify Which Structure On The Diagram Would Be F Chegg Com
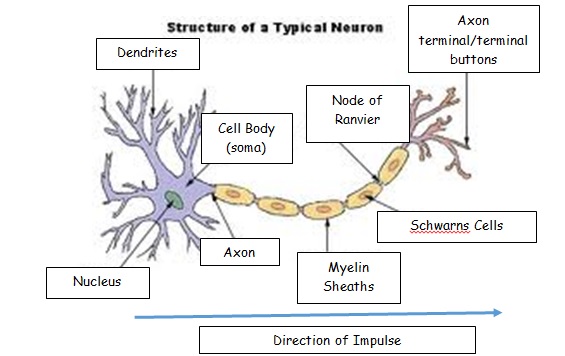
What Is A Motor Neuron Motor Nerves Innervation

Sensory Relay And Motor Neurones Edexcel Int A Level Biology Teaching Resources

9 Describe The Structure Of The Human Nervous System Portfolio Project
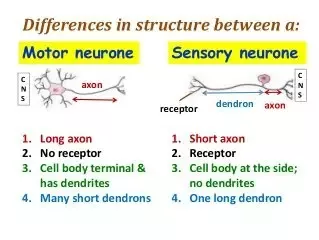
What Is The Difference Between Sensory Neuron And A Motor Neuron Quora
The Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Psychology Hub
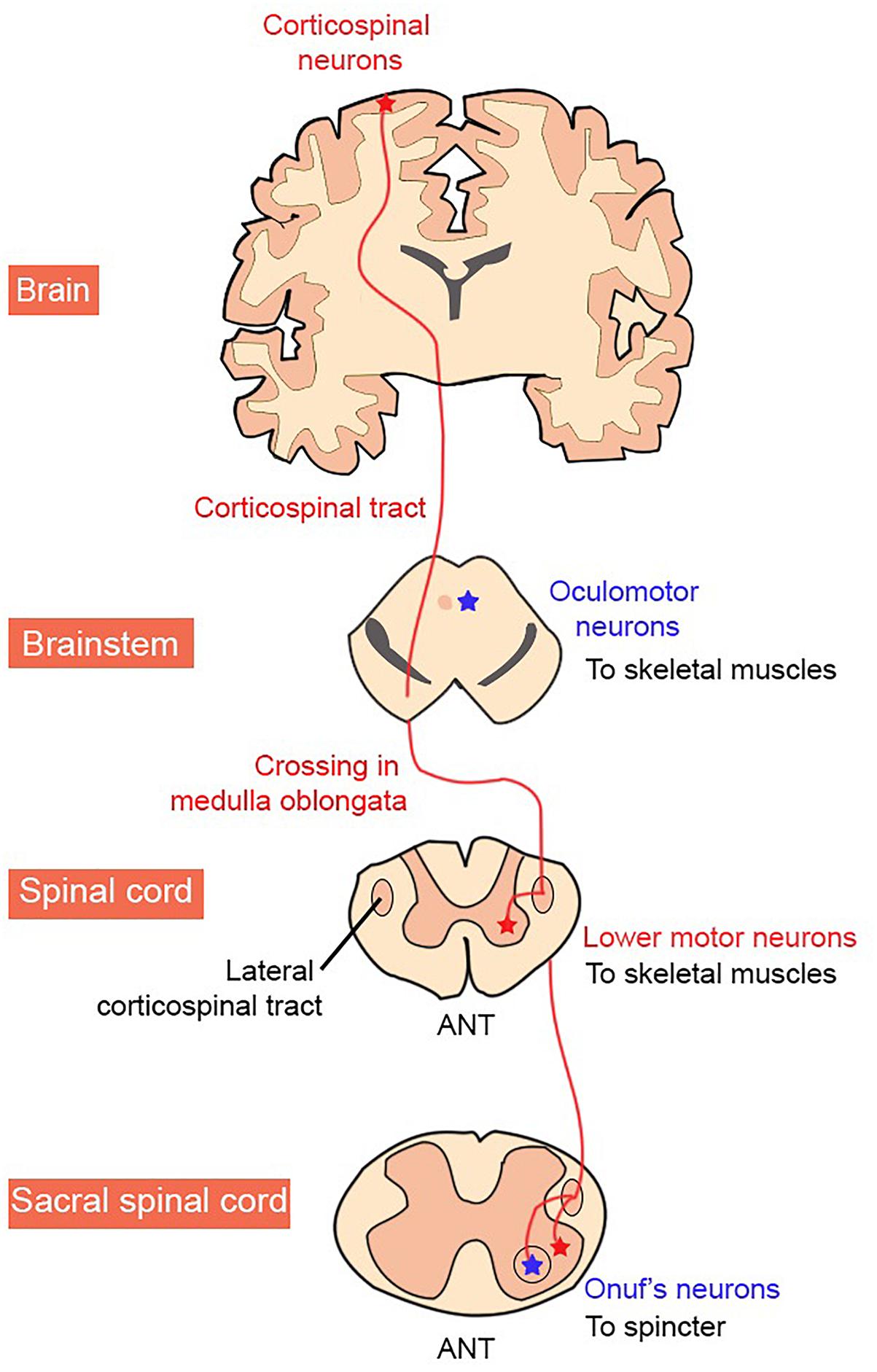
Frontiers Motor Neuron Susceptibility In Als Ftd Neuroscience

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
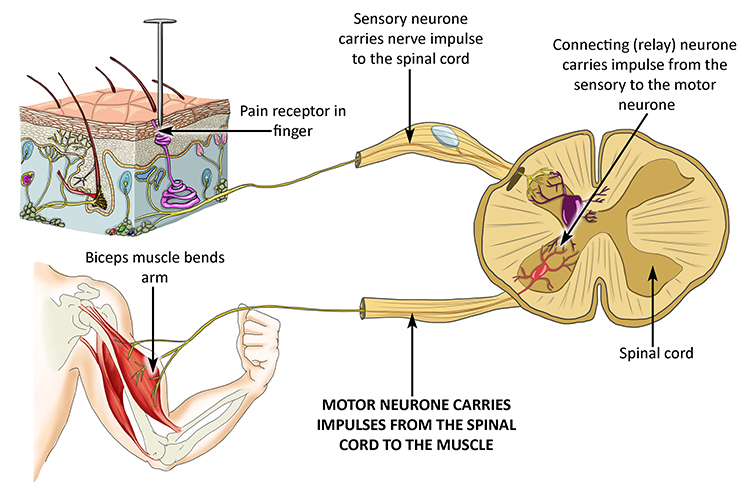
Motor Neurones Sensory Neurones And Relay Neurones

Structure Of Neurones

View Image

Chapter 15 Coordination Ppt Download
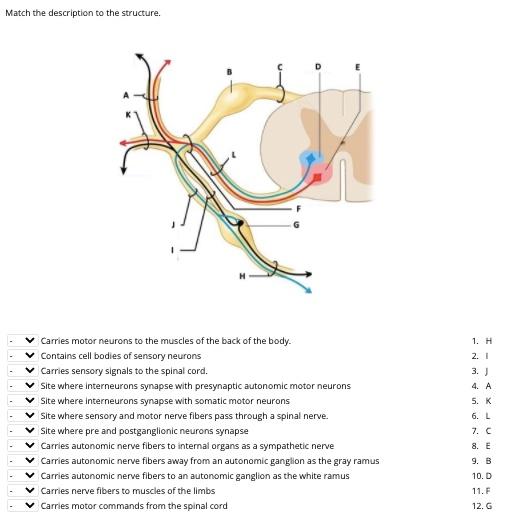
Solved Match The Description To The Structure D Carries Chegg Com

Motor System I Peripheral Sensory Brainstem And Spinal Influence On Anterior Horn Neurons Neupsy Key
1
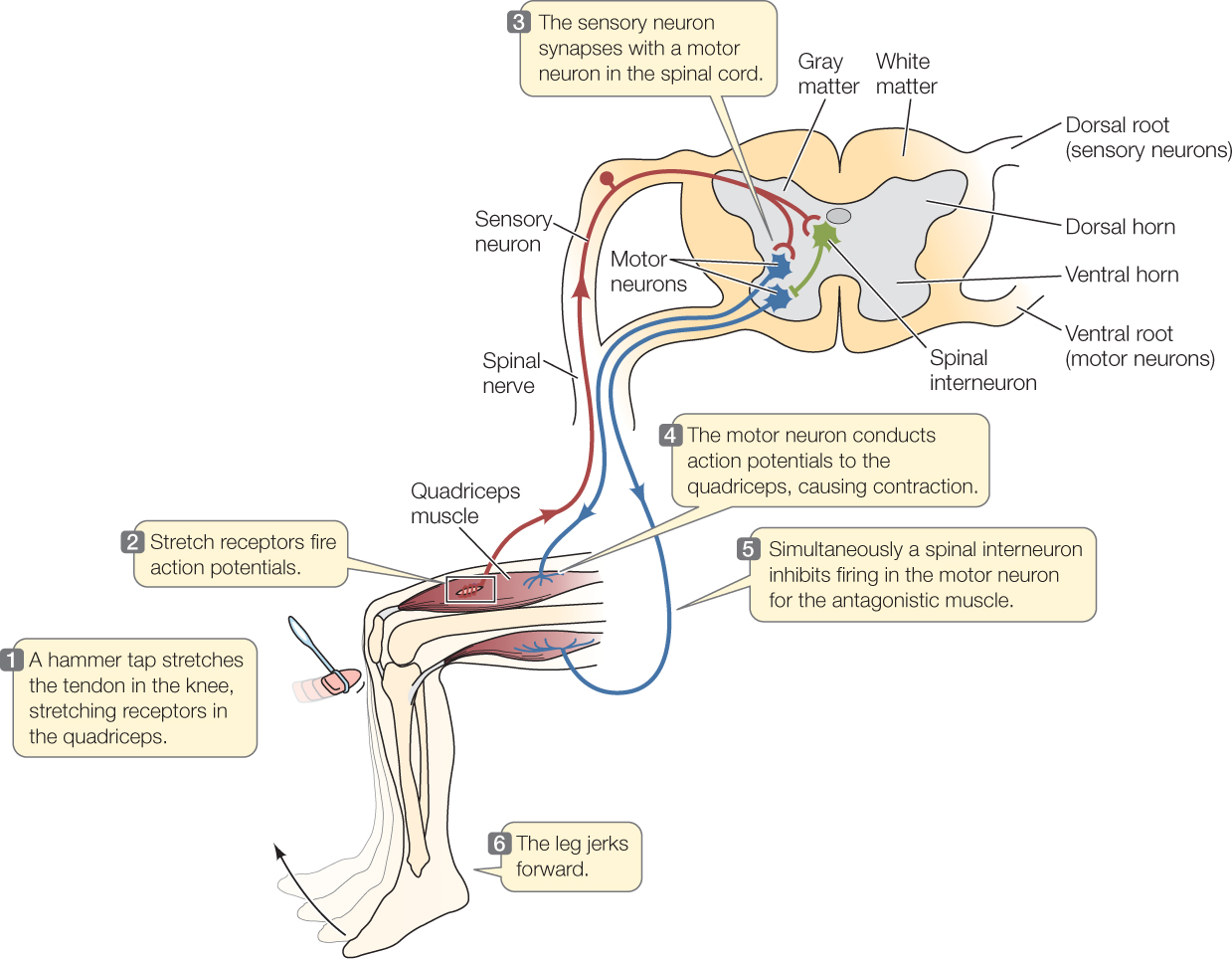
Hillis2e Ch34
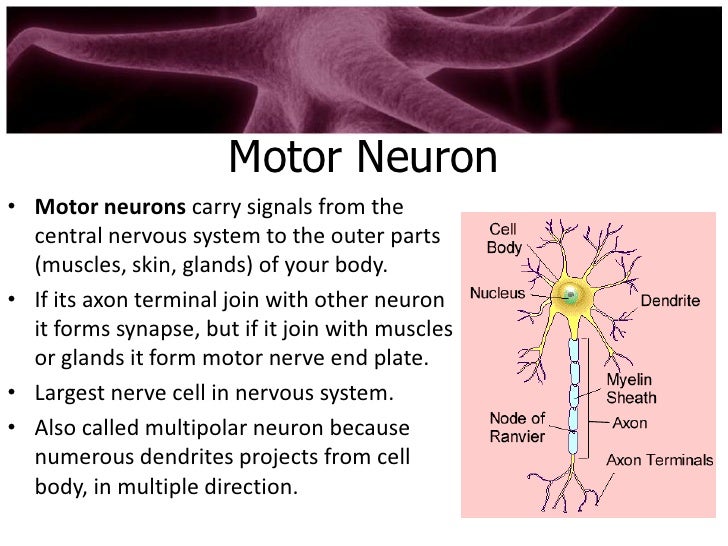
Types Of Neuron
Axon Wikipedia
Neurons And Neural Pathways Ppt Video Online Download

Stimulus Response Bioninja

The Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Psychology Hub

The Central Nervous System Consists Of The Brain And The Spinal Cord Sensory Information Is Received By Them And Interpreted And Then Processed Responded Ppt Download

Doc A The Structure Of A Neuron Guvvala Reddy Academia Edu
Labelled Diagram Of Motor Neuron Trusted Wiring Diagrams

Motor Neuron Nerve Cell Britannica
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neuron Byju S

Neurons Boundless Psychology
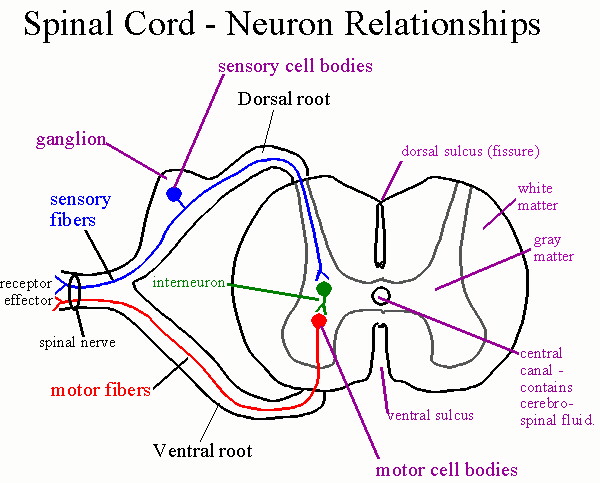
Biol 237 Class Notes The Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerves

Chapter 4 The Cytology Of Neurons Ppt Video Online Download
Do Motor Neurons Have The Same Structure As Sensory Neurons Quora

5 8 1 Describe The Structure And Function Of Sensory Relay And Motor Neurones Including The Role Of Schwann Cells And Myelination A Biology

Sensory Neuron Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
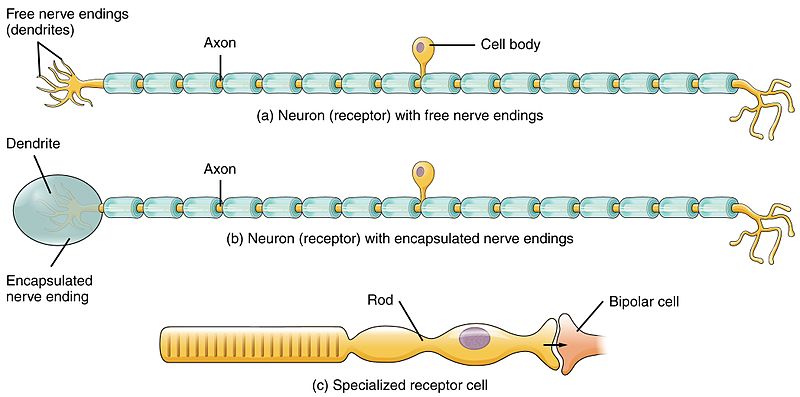
Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neurons Definition Structure Function Characteristics

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
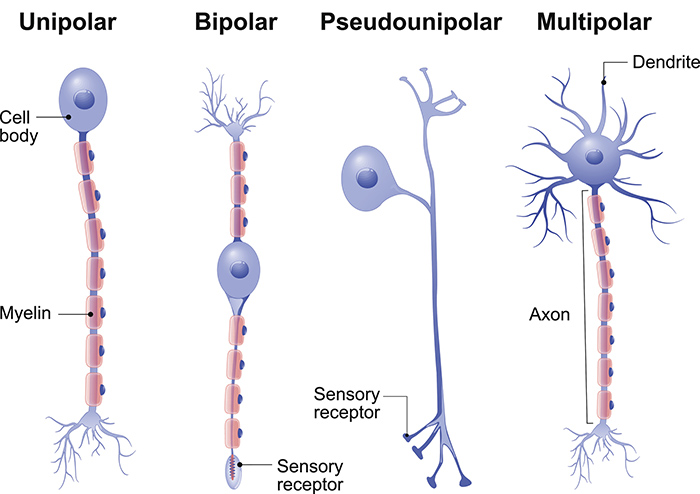
Types Of Neurons Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
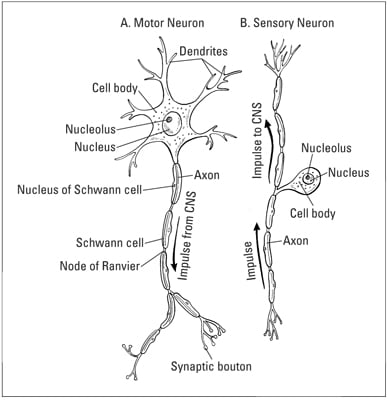
What S The Basic Structure Of Nerves Dummies

Reflexes Nervous System Structure And Function Mcat Content

Structural And Functional Differences Between Somatic Motor And Sensory Neurones University Miscellaneous Marked By Teachers Com

Upper Motor Neuron And Lower Motor Neuron Syndromes Bone And Spine
Q Tbn And9gct9yycisgxxqqrh9bdzlunzk8h1e Wefctwea2dwpk Usqp Cau

Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neurons Read Biology
Sensory Relay And Motor Neurons Teaching Resources

Alpha Motor Neuron Wikipedia
Interneuron Wikipedia

Neuron Anatomy Types Of Motor Neurons Somatic These Are Responsible For Both Human Anatomy And Physiology Nervous System Anatomy Brain Anatomy

Neurons Boundless Psychology
Neuron Structure And Classification Brooke Hamilton Neural Tissue
Motor Nerve Wikipedia
Labeled Diagram Of Motor Neuron Schematics Wiring Diagrams
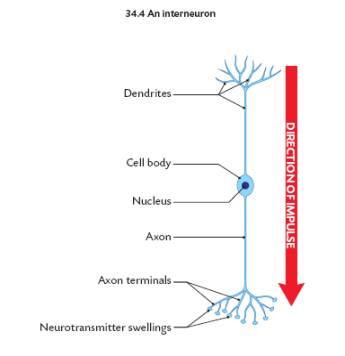
The Nervous System
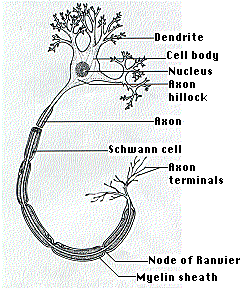
Neurons

Structure Of Sensory And Motor Neurones Cie International A Level Biology Teaching Resources
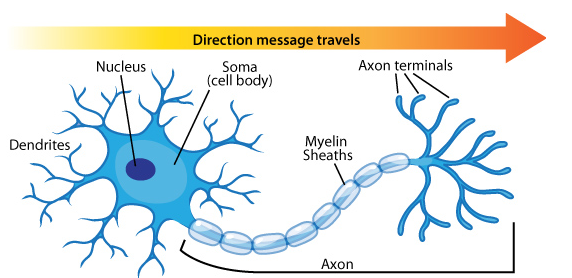
Structural Functional Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neuron Viva Differences

Types Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Stock Illustration

Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
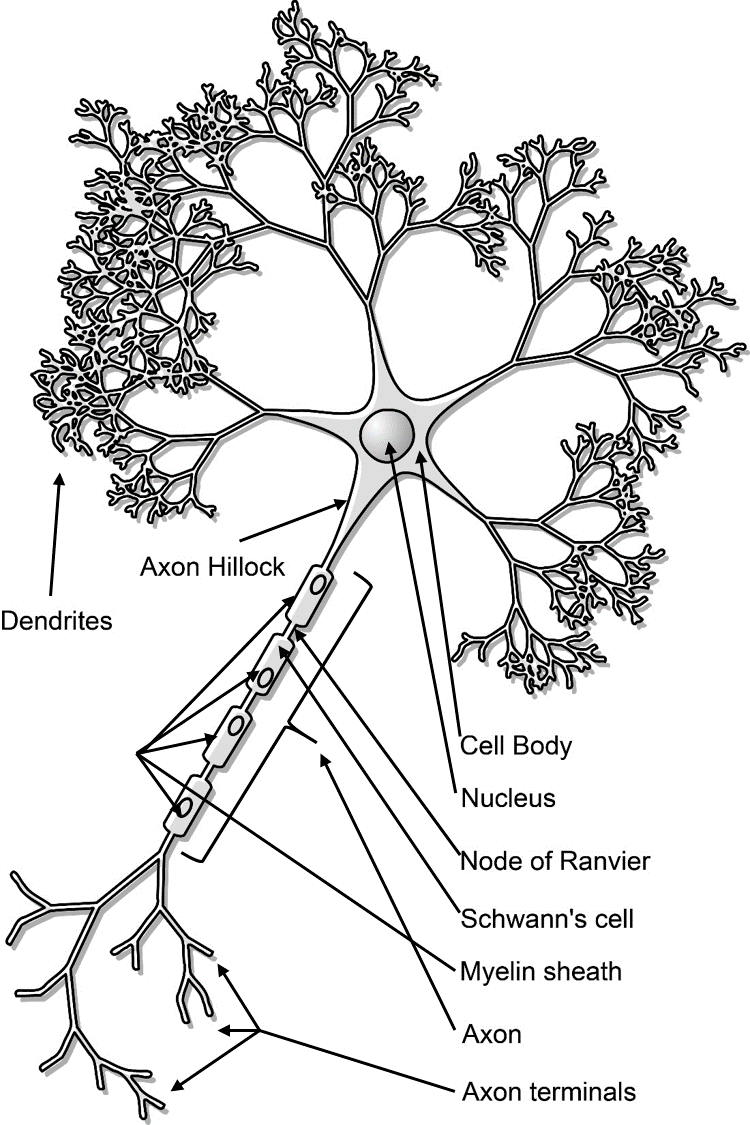
Neuron Structure And Classification

Ch 11 Types Of Neurons
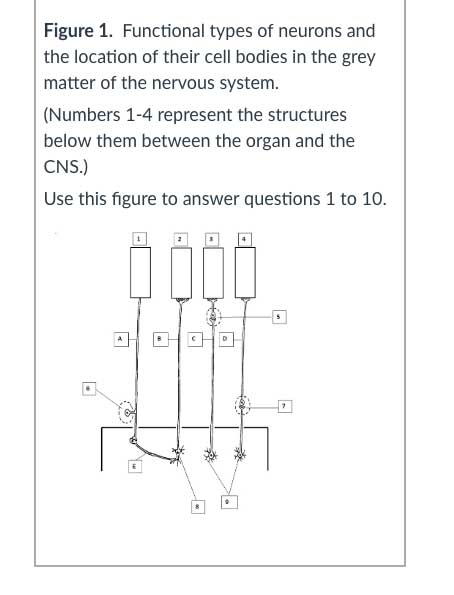
Solved What Structure On The Diagram Would Be Found Betwe Chegg Com

Neuron Structure And Function Sensory Neurons Association Neurons Motor Neurons Youtube

12 3 The Function Of Nervous Tissue Anatomy Physiology

Nervous System Bioninja
Q Tbn And9gcsj4ebgqe3osyhkmjphb3knfwjho5zkv2vak6gsjwjhqiuigv61 Usqp Cau
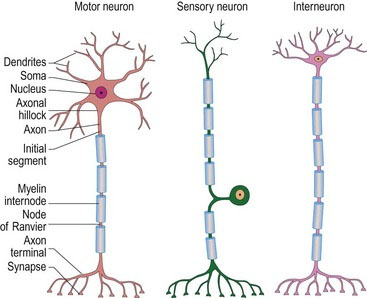
Neurohistology Physiology And Supporting Structures Veterian Key
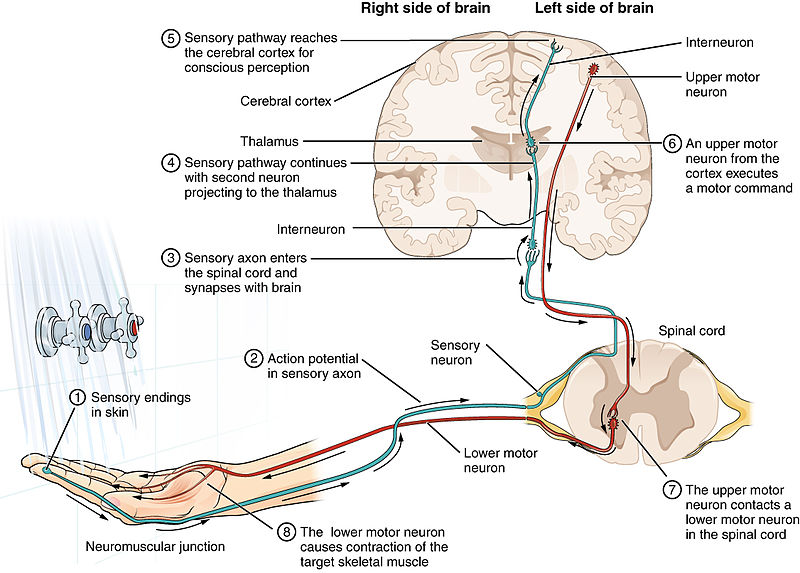
11 3 Neurons And Glial Cells Biology Libretexts
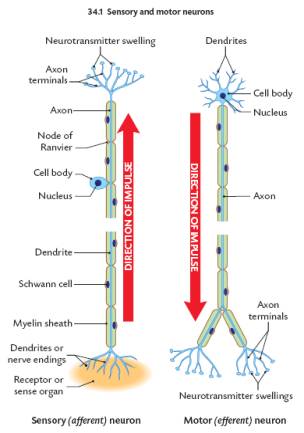
The Nervous System

Motor Neuron Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Sensory Neuron Wikipedia

What Is The Structure Of A Sensory Neuron Quora
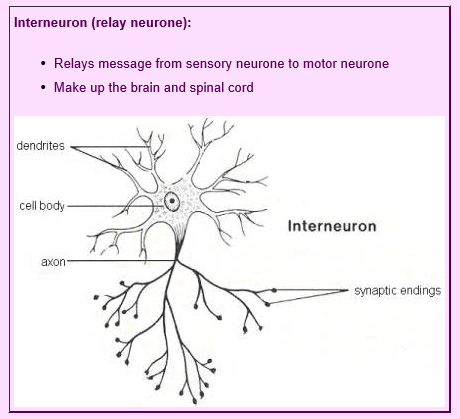
The Central Nervous System Structure And Functions

Relationship Between Structure And Function Of A Motor Neurons Biochemstyles
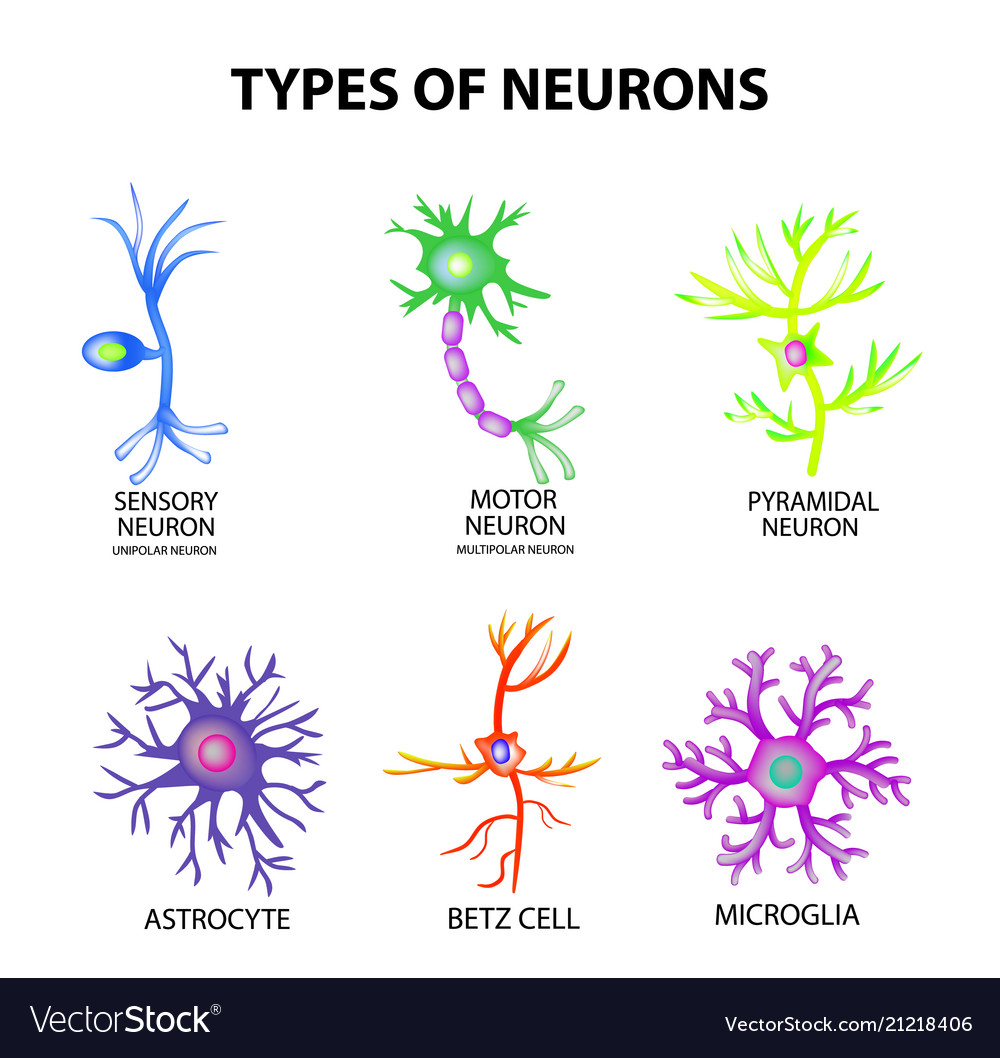
Types Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Vector Image
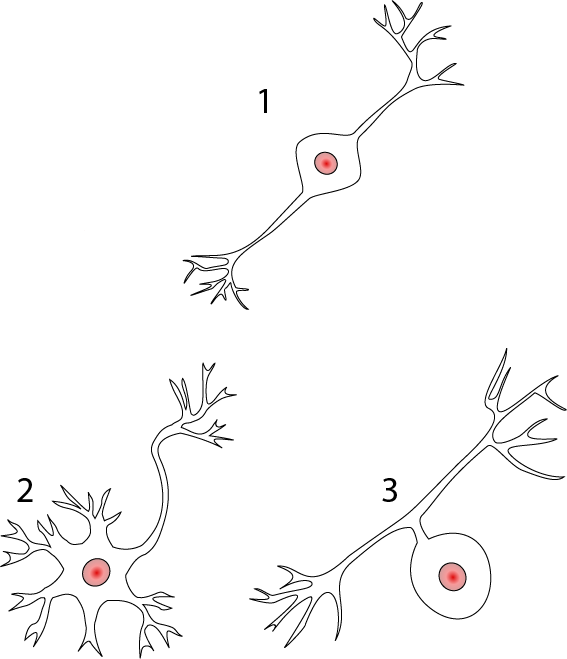
Neuron Structure And Classification

Difference Between Sensory And Motor Neurons Definition Structure Function Characteristics Motor Neuron Neurons Human Anatomy And Physiology

Sensory Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



